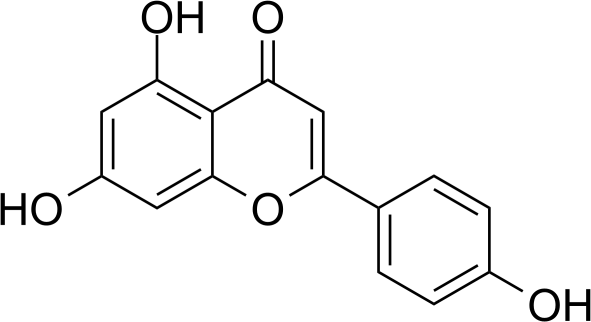
Most of us are aware that Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) levels decrease during aging, and are involved in age related metabolic decline. Furthermore many people know the most popular anti-aging supplement NMN (precursor to NAD+), but few people know about Apigenin.
It is also abundant in many medicinal mushrooms like Agaricus blazei, shiitake, and maitake.
Several plant bioactive compounds have exhibited functional activities that suggest they could play a remarkable role in preventing a wide range of chronic diseases. The largest group of naturally-occurring polyphenols are the flavonoids, including apigenin.
Extensive studies have focused on its antineoplastic, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-stress, pro-mitochondrial, neuroprotective, and general adaptogenic effects.
Most of us are aware that Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) levels decrease during aging, and are involved in age related metabolic decline. Furthermore many people know the most popular anti-aging supplement NMN (precursor to NAD+), but few people know about Apigenin.
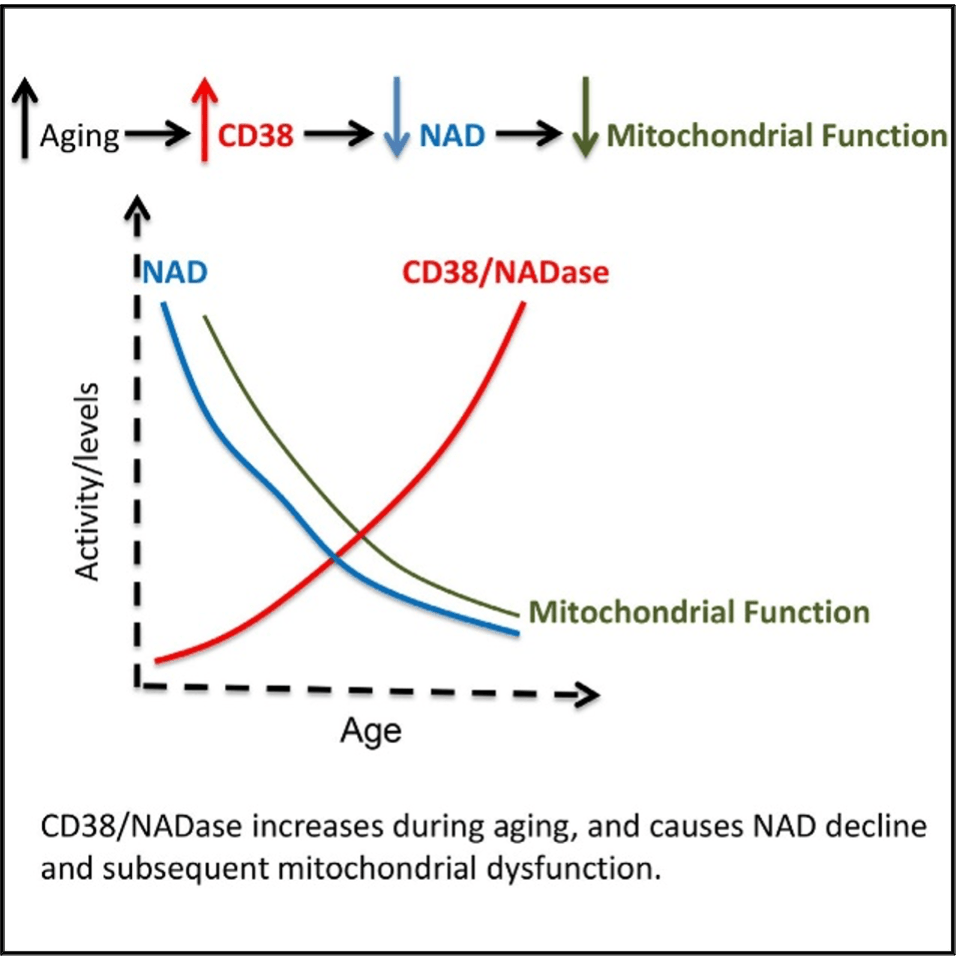
Figure1: From study “CD38 dictates age-related NAD decline and mitochondrial dysfunction through a SIRT3-dependent mechanism”
NAD boosting has emerged as one of the key strategies for improving our healthspan.
However, we cannot simply boost our NAD levels by taking NAD supplements, as NAD’s molecule is so large and bulky (to enter each cell to be effective) that we have to take precursor molecules.
These precursors (such as NMN, NR, etc) are converted into NAD within the human body, making them popular in the anti-aging and healthspan community.
Why do our NAD levels decline as age when they are vital to our human body? By exploring and reading various scientific studies, we may get answers from one enzyme-CD38 to get the truth!
From the study “CD38 dictates age-related NAD decline and mitochondrial dysfunction through a SIRT3-dependent mechanism we can clearly see (figure 1) that as we age, the NAD level decline while at the same time CD38 keeps increasing.
A question is raised: Is CD38 related to the rapid consumption of NAD?
Two new studies by Chini et al. and Covarrubias et al. in Nature Metabolism show that CD38 expression in macrophages induced by senescence-associated inflammation accounts for the age-related decline in NAD+ levels.
Referring to figure 2 below from the study: When aged cells stop growing and replicating, a phenomenon called senescence, secrete molecules associated with inflammation in a process called a senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP).
The presence of these molecules increases with age and induces the presence of CD38 on immune cells. This is how increased CD38 levels from aging-associated inflammation lead to progressive NAD+ level reductions through the SASP cellular loop.
CD38 enzyme levels increase as a result of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) linked with aging in the liver. This leads to increased consumption of NAD+ within and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) outside of immune cells called M1 macrophages.
For these reasons, CD38 on M1 macrophages is a potential therapeutic target for preventing age-related NAD+ decline.
Simply supplementing NMN can effectively store and increase NAD levels in the human body, but how can we protect NAD more effectively? Inhibiting CD38 must be put in the first place!
In a significant recent research study “Flavonoid apigenin is an inhibitor of the NAD+ase CD38: Implications for cellular NAD+ metabolism, protein acetylation, and treatment of metabolic syndrome”, we now know that supplemental Apigenin can inhibit CD38 directly, and result in increased NAD levels.
It was found to ‘switch off’ the pro-inflammatory genes leading to the inflammation problem, driving the response of those macrophages involved in expressing CD38. This also shows up in better maintenance of your protein regulation, as your genes become less ‘acetylated’, and more youthful as a result.
Therefore, Apigenin must be the best companion of NMN. Taking Apigenin together with NMN will take a better effect on longevity.
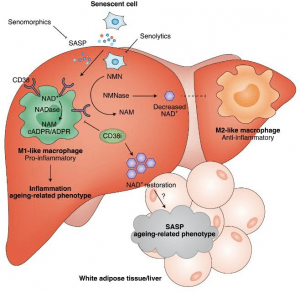
Figure2: From Nature Metabolism-Inflammation associated with aging induces CD38 enzyme activity in M1 macrophages that consume NAD+.
Apigenin is known to offer a range of health benefits, from supporting heart and brain health to promoting healthier skin, to improving healthspan and protects against a wide variety of cancers. Most of the studies involving the flavonoid use animal models, but they highlight the potential mechanisms and benefits of this plant nutrient.
Flavonoids are widely known for their antioxidant properties, and a number of studies show that apigenin, in particular, has significant antioxidant effects. It’s also an effective anti-inflammatory agent compared to other flavonoids.
Because of its antioxidant effects, the flavone is used to promote healthy aging, increase our healthspan and utilised to boost skin health. Topical apigenin is even used to fight acne and promote skin cell growth.
Reports suggest that apigenin has “reverse antibiotic” activities against some bacteria, which means that it may be active against antibiotic-resistant bacteria and help reverse bacterial resistance. Researchers believe that the phytonutrient could be a candidate as a new antibiotic or as a dietary supplement to enhance the performance of antibiotics.
The nutrient also has proved to inhibit multiple viruses, including herpes; hepatitis C; influenza; hand, foot and mouth disease; and African swine fever.
Because of its anti-inflammatory effects, apigenin is able to reduce pain and discomfort related to inflammatory issues. This includes pain from digestive problems, infections, immune responses and migraine pain.
The flavonoid has been shown to decrease the release of cytokines, which can overproduce and lead to disease.
Apigenin supports cardiovascular health by reducing blood pressure and inflammation. Animal models show that it has cardioprotective effects in rats with heart damage. One animal study found that apigenin protected rats against heart attack by reducing edema, cell death and oxidative stress.
Apigenin has neuroprotective effects. Research published in Neural Regeneration Research found that apigenin has cognition-enhancing effects because of its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In mice with Alzheimer’s disease, it was able to improve memory and learning deficits, and in humans it suppressed inflammatory mediators.
This flavone is known for its relaxing and sedative effects. It has been shown to reduce cortisol levels, helping prevent the body’s response to chronic stress. This explains why chamomile tea can have beneficial effects on anxiety and help aid relaxation and sleep.
Apigenin also has been shown to improve depression in rodents. Treatment with the flavone was able to elevate immobility time in mice that were induced by chronic corticosterone treatment.
Animal studies suggest that apigenin improves insulin resistance and can be helpful for people with diabetes. One report found that the flavone improved impaired glucose tolerance and significantly decreased insulin resistance.
Apigenin is also a very potent anti-cancer compound. It beneficially protects against a wide variety of cancers with high selectivity for cancer cells as opposed to non-cancerous cells.
Several experimental and biological studies suggest that apigenin works as an anticancer agent. A report published in Phytotherapy Research found that the flavonoid exhibits cell growth arrest and apoptosis in many types of tumors, including lung, liver, colon, prostate, pancreatic, breast, skin, blood and cervical.
Anticancer research further explores how apigenin plays a role in several cancer signaling pathways and should generate interest as a possible chemotherapeutic modality due to its low toxicity and effects on normal versus cancerous cells.
Lab studies suggest that apigenin plays a role in testosterone synthesis and blocks signaling of testosterone repressing proteins. Because of its potential impact on hormone levels, it has become more popular to use apigenin for bodybuilding efforts. This may help with muscle growth, strength and energy levels. In this case, apigenin supplements are used to increase testosterone and potentially block estrogen production.
Aigenin has a very high safety threshold and is considered safe even at high doses, and no toxicity has been reported. Nonetheless, at high doses, it can trigger muscle relaxation and sedation.
If you experience stomach discomfort after consuming apigenin, then discontinue use immediately.
Topicals containing the nutrient may cause skin irritations in some people, so if you experience any adverse reaction, stop using the product.
More research is needed to fully understand the safety of high apigenin doses. Before using extracts or supplements for a health condition, speak to your health care provider.
For Healthspan and Anti Aging, a daily dose of two pure Apignein capsules (2 x 250mg) which is often used to regulate CD38 levels, and help boost NAD+ levels in the body. Each bottle contains 60 capsules of 250mg per capsule. You may take the capsules with or without food.
For anxiolytic effects, doses in the range of 2.4 to 8.1 mg/kg bodyweight (ie: 75kg person = 180mg to 600mg) may be effective without sedation, and higher doses may induce sedation in addition to reductions in anxiety. This dose is derived from a study in mice and is post-conversion.
The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/20/6/1305
Flavonoid Apigenin Is an Inhibitor of the NAD+ase CD38
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3609577/
CD38 dictates age-related NAD decline and mitochondrial dysfunction through a SIRT3-dependent mechanism.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4911708/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27304511/
CD38-expressing macrophages drive age-related NAD+ decline
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-020-00292-5?proof=t%252Btarget%253D
CD38 ecto-enzyme in immune cells is induced during aging and regulates NAD+ and NMN levels
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-020-00298-z?draft=journal&proof=t%252Btarget%253D
Senescent cells promote tissue NAD+ decline during ageing via the activation of CD38+ macrophages
https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-020-00305-3?draft=journal&proof=t%252Btarget%253D
Apigenin: A dietary flavonoid with diverse anticancer properties
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030438351730678X
Role of Apigenin in Cancer Prevention via the Induction of Apoptosis and Autophagy
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5207605/
Structure and Enzymatic Functions of Human CD38
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17380198/
A Review on Flavonoid Apigenin: Dietary Intake, ADME, Antimicrobial Effects, and Interactions with Human Gut Microbiota
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6817918/
Apigenin and naringenin regulate glucose and lipid metabolism, and ameliorate vascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetic rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26801071/
Effects of apigenin on steroidogenesis and steroidogenic acute regulatory gene expression in mouse Leydig cells
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20537519/
Apigenin: A dietary flavonoid with diverse anticancer properties
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29097249/
Curcumin and Apigenin – novel and promising therapeutics against chronic neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4590215/
Apigenin reverses depression-like behavior induced by chronic corticosterone treatment in mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26826594/
Pharmacological profile of apigenin, a flavonoid isolated from Matricaria chamomilla
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10751547/
Apigenin as an anticancer agent
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32059077/