Japanese scientists find that NMN reduces blood vessel stiffness in middle-aged adults with higher-than-average weight and blood glucose levels.
By Victor Ciardha Original Article: www.nmn.com
Highlights:
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a promising anti-aging therapeutic, as it promotes the synthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a molecule that declines with aging. NMN’s anti-aging potential stems from model organism studies showing that it prolongs lifespan and mitigates age-related disease. However, the degree to which NMN slows the aging process in humans remains unclear.
In a preprint article (not yet peer-reviewed) shared on Research Square, Katayoshi and colleagues from the DHC, a corporation in Japan that sells skincare products, report the findings of a clinical trial testing the effects of NMN on humans. The results showed that NMN tends to reduce arterial stiffness in healthy middle-aged adults but without statistical significance. However, statistically significant reductions in arterial stiffness were observed in individuals with above-average weight and blood glucose levels. Furthermore, NMN was calculated to reverse blood vessel aging by two years.
NMN Reduces Blood Vessel Stiffness
When young, our blood vessels are highly elastic, able to modulate blood flow to active organs. However, with age, our blood vessels lose elasticity and become stiff, making our hearts work harder. To test the effects of NMN on blood vessel aging, Katayoshi and colleagues measured blood vessel (artery) stiffness from thirty-four healthy adults aged 40-59 years who took 250 mg of NMN for twelve weeks. They assessed blood vessel stiffness by measuring how fast blood moves through an artery near the ankle. The researchers found that, while not statistically significant, NMN reduced blood vessel stiffness.
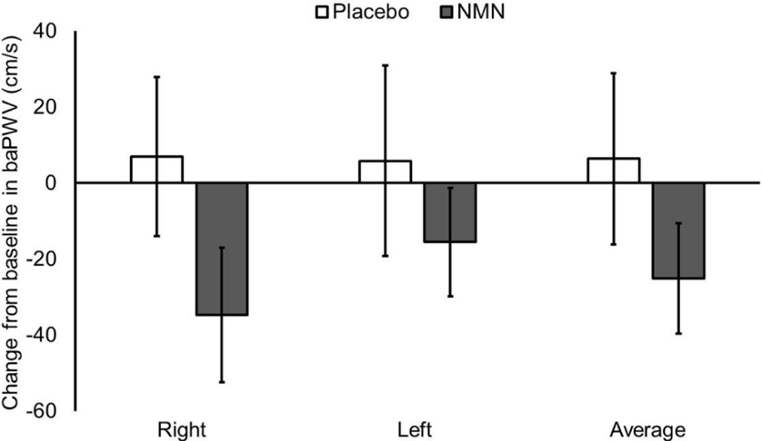
(Katayoshi et al., 2022 | Research Square)
NMN Tends to Reduce Blood Vessel Stiffness in Healthy Individuals. Participants treated with NMN (gray) have lower brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) values than untreated participants (Placebo) in the right and left leg, indicating reduced blood vessel stiffness.
Since high blood pressure, obesity, and high blood glucose levels are cardiovascular disease risk factors, Katayoshi and colleagues separated participants based on their blood pressure, body mass index (BMI), or blood glucose level. Participants with above-average BMI or blood glucose levels had reduced blood vessel stiffness after NMN treatment, suggesting that NMN improves vascular health in those with high BMI and blood glucose.
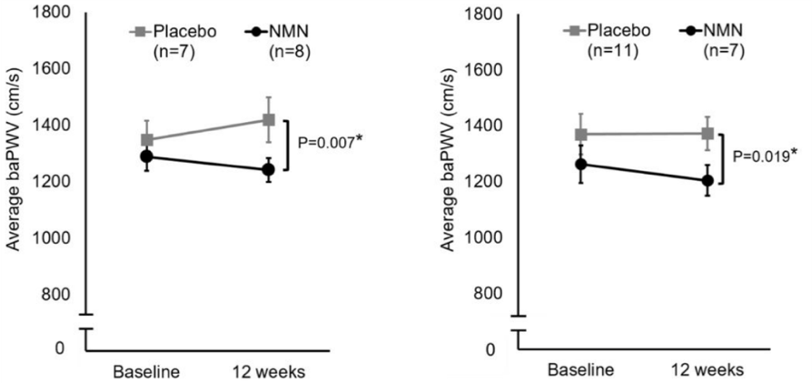
(Katayoshi et al., 2022 | Research Square)
NMN Reduces Blood Vessel Stiffness in High Weight and High Blood Glucose Individuals. Participants treated with NMN (gray) have significantly lower brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) values than untreated participants (Placebo) in the right and left leg, indicating reduced blood vessel stiffness.
Scientists have been able to calculate the age of our organs and tissues using various indicators, such as blood vessel stiffness. Using such calculations, Katayoshi and colleagues estimated that NMN makes blood vessels approximately two years younger in middle-aged adults. The precise process by which NMN improves blood vessel aging, however, remains unclear.
Since reduced blood vessel stiffness is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, the findings from Katayoshi and colleagues suggest that NMN supplementation could reduce cardiovascular disease risk. Only one other study has tested the effects of boosting NAD+ on blood vessel stiffness. In the study, 1000 mg of nicotinamide riboside (NR) was given to middle-aged adults for 6 weeks, resulting in a tendency to reduce blood vessel stiffness. Thus, these two studies have similar results, and it may be that a larger study could result in statistically significant findings.
NMN Reverses Multiple Aspects of Human Aging
Clinical trials testing the effects of NMN on human aging have only begun in the last few years. So far, NMN has been shown to increase insulin sensitivity, improve sleep and physical performance, enhance exercise endurance, improve skin health, increase walking speed, and increase strength in middle-aged and older adults. These clinical trials suggest that much of the research demonstrating the anti-aging effects of NMN on animals is translatable to humans. Still, more long-term studies are needed to assess adverse effects that may occur with chronic NMM supplementation. If NMN proves to be safe in the long-term, larger studies may even show more significant anti-aging effects.
Story Source
Takeshi Katayoshi, Sachi Uehata, Noe Nakashima et al. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism and arterial stiffness after long-term nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 29 July 2022, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square [https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1802944/v1]
Journal Reference
Zieman SJ, Melenovsky V, Kass DA. Mechanisms, pathophysiology, and therapy of arterial stiffness. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 May;25(5):932-43. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000160548.78317.29. Epub 2005 Feb 24. PMID: 15731494.
Researchers from the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis show that the enzyme behind NMN biosynthesis – NAMPT – reverses metabolic derangements in obese mice.
By Jonathan D. Grinstein, Ph.D. www.nmn.com
Highlights
Intermittent fasting and caloric restriction improve metabolism and inflammation in mice and humans. That’s why both intermittent fasting and caloric restriction have been pursued as promising means by which to abate diseases of aging, overnutrition, and neurodegeneration. Calorie restriction abates aging and cardiometabolic disease by activating metabolic signaling pathways, including the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) synthesis pathway.
Published in Nature Communications, researchers from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis show that NAMPT – an enzyme necessary for synthesizing the NAD+ precursor NMN – in the liver drives critical aspects of the fasting response. On the one hand, mice lacking NAMPT in liver cells exhibit defective thermal regulation during fasting and are sensitized to diet-induced glucose intolerance. On the other hand, increasing levels of NAMPT in liver cells induces fat browning, improved glucose balance, and attenuated high blood fat levels (dyslipidemia) in obese mice. This work shows that modulating NAD+ levels in liver cells can potentially mitigate fasting-associated disease.
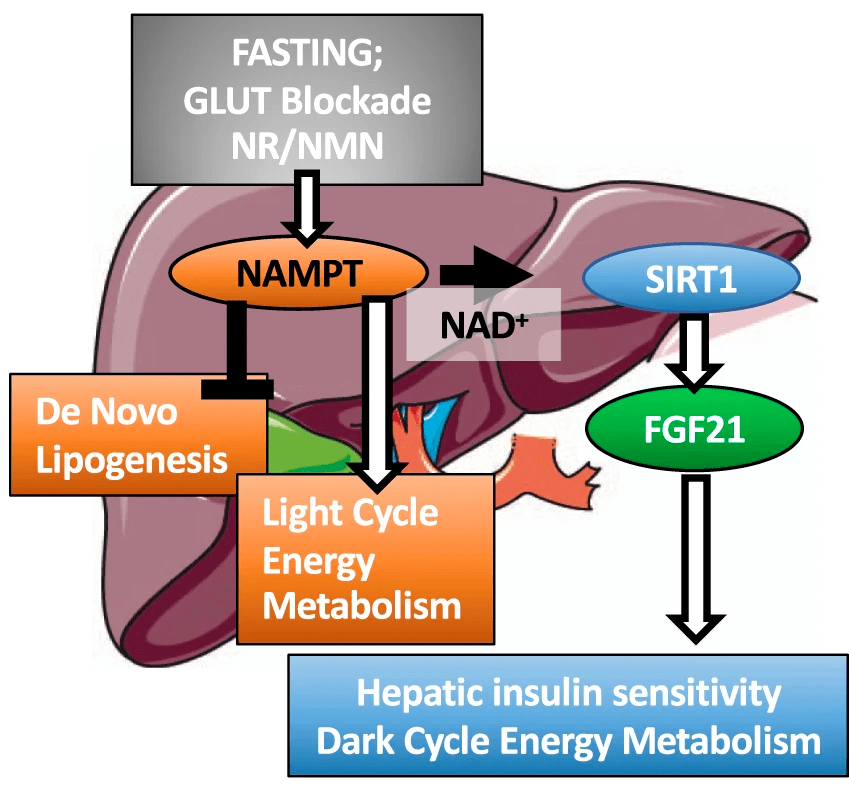
(Higgins et al., 2022 | Nature Communications) NAMPT in the liver balances energy metabolism. Liver cell NAMPT activation promotes light- and dark-cycle energy metabolism and liver insulin sensitivity while blocking the formation of fat (de novo lipogenesis). NAMPT can be activated by blocking glucose transporters (GLUT) or through supplementation with the NAD+ precursors nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). NAMPT = nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, SIRT1 = sirtuin 1, FGF21=fibroblast growth factor 21.
The Liver Is Central to Metabolic Regulation
The liver is uniquely positioned at the nexus between blood coming from the digestive system and blood being sent back to the heart to be pumped to the brain, limbs, and the rest of the body. Here, the liver can sense, coordinate, and transition between different states of metabolism that depend on feeding or the lack thereof (also known as fasting). Nutrient withdrawal creates an adapt-or-perish proposition for an organism in general and for liver cells in particular. The lack of sugar forces a reliance upon fat breakdown throughout the body, which gets metabolized in the liver. When this occurs, the liver needs to make several key adjustments. NAD+ synthesis unifies the adaptive responses to each of these stresses in the nutrient-restricted liver. Accordingly, NAD+ protects against diseases ranging from aging and neurodegeneration to diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Liver NAMPT Is Necessary for Fasting Benefits
In this study, the Washington University of Medicine in St. Louis researchers dissect how NAMPT in liver cells modulates metabolic balance. Higgins and colleagues demonstrate that liver NAMPT mediates a key liver signaling cascade during fasting. The study shows that fasting and glucose transport inhibition upregulates NAMPT in the liver, while liver-specific NAMPT deficiency impairs several key fasting metabolic processes. More specifically, mice lacking NAMPT in the liver show defects in glucose metabolism, whereas viral-mediated increases in liver NAMPT enhance thermogenesis and glucose metabolism in diet-induced and genetically obese models. These findings show that liver NAMPT levels are essential to protect against diet-induced glucose intolerance and to elicit the metabolic benefits of fasting.
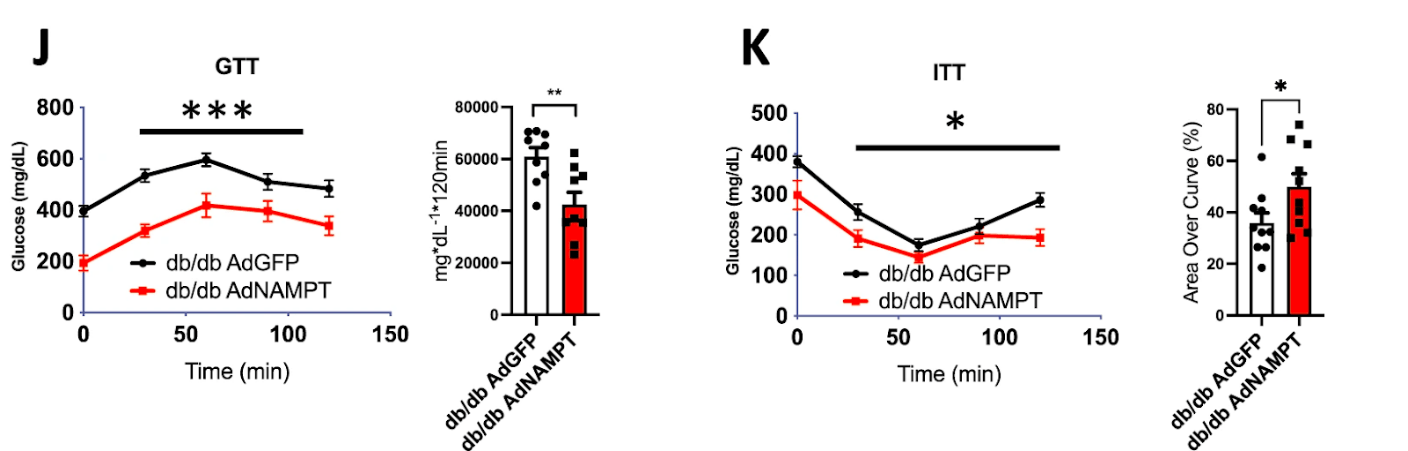
(Higgins et al., 2022 | Nature Communications) Liver NAMPT enhances glucose homeostasis in diabetic mice. Increased levels of NAMPT in obese, diabetic mice (db/db AdNAMPT) led to lower plasma glucose throughout both glucose and insulin tolerance testing, indicating improved glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
Higgins and colleagues found that raising NAMPT levels in obese diabetic mice increased fat tissue browning markers. Fat tissue (usually white) turns brown when it is thermogenically active, meaning that it generates more heat while burning calories. Along these lines, mice with elevated liver NAMPT had higher thermogenesis levels than controls. Raising liver cell NAMPT induced increased heat production and gas exchange – more oxygen in and carbon dioxide out during breathing – in mice during both light- and dark cycles, whereas NAMPT deletion led to dark-cycle thermic defects. The data indicate that liver cell NAMPT signaling distinguishes between light- and dark-cycles when modulating energetic control.
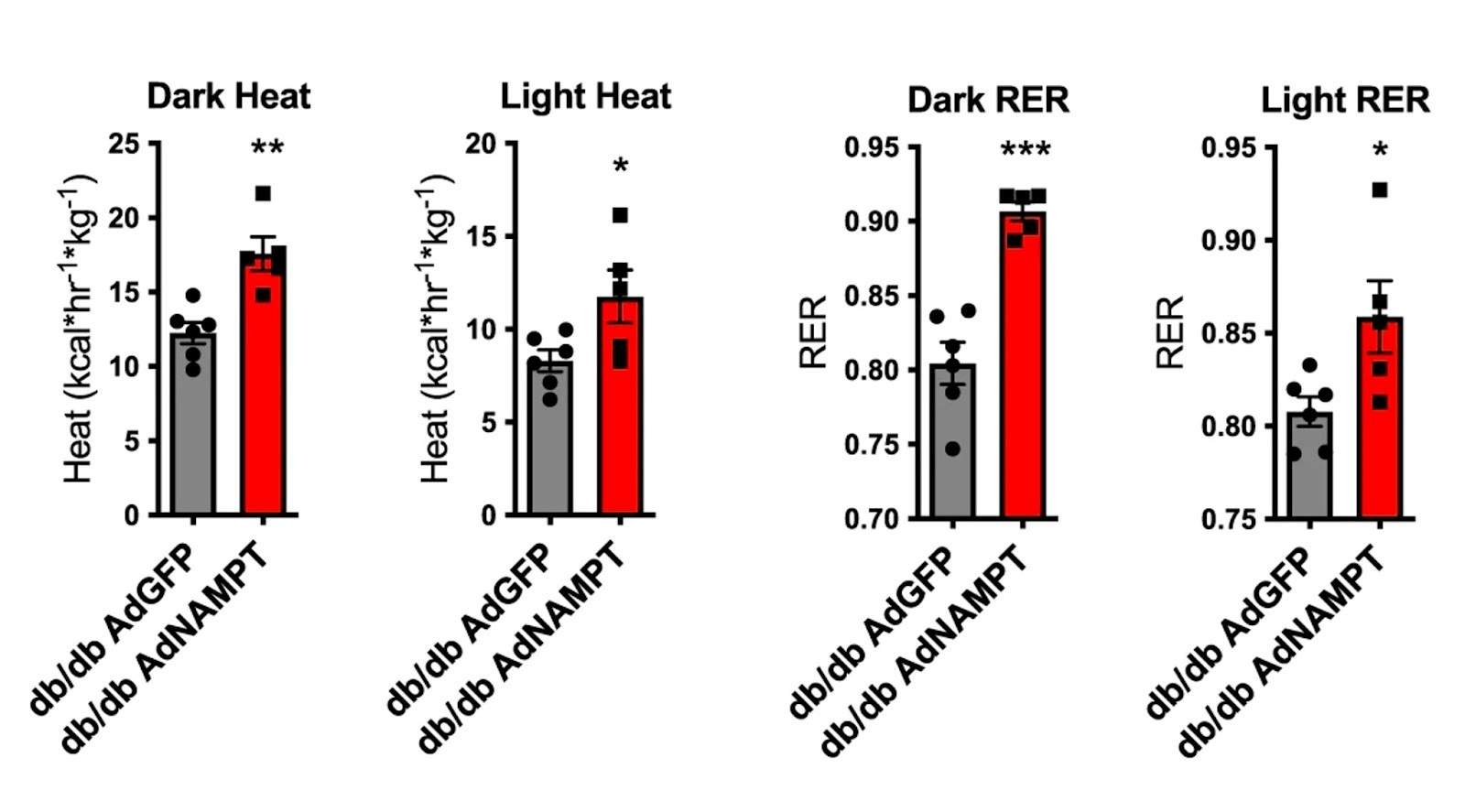
(Higgins et al., 2022 | Nature Communications) NAMPT induces fat tissue browning and thermogenesis in diabetic mice. To measure the role of NAMPT on thermogenesis and energy regulation, diabetic mice (db/db) were treated with a virus carrying NAMPT (AdNAMPT). Compared to controls, these mice exhibited significantly greater dark- and light-cycle thermogenesis and respiratory exchange rates (RER).
Higgins and colleagues conclude that NAMPT in the liver exerts broad fasting-mimetic effects downstream of generalized fasting and glucose transport inhibition in liver cells. This study suggests that metabolic disease can be intervened at the level of NAD+ biosynthesis via NMN. It is possible that NAMPT activation in the liver can fight against aging, obesity, and other fasting-responsive diseases. Interestingly, there are some compounds that activate NAMPT like SBI-797812, which turns NAMPT into a “super catalyst” that more efficiently generates NMN. Of note, mice dosed with SBI-797812 show elevation in liver NAD+. For all we know, this could be the basis for that long-sought-after miracle fasting pill.
Story Source Higgins CB, Mayer AL, Zhang Y, Franczyk M, Ballentine S, Yoshino J, DeBosch BJ. SIRT1 selectively exerts the metabolic protective effects of hepatocyte nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase. Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 28;13(1):1074. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28717
Chinese scientists find that NMN protects against intestinal damage caused by radiation — commonly used to treat elderly cancer patients.
By Victor Ciardha 2022. Original Article: www.nmn.com
Highlights:
Radiotherapy is commonly used to treat elderly cancer patients who are often too frail to undergo surgery or receive chemotherapy. However, 60 to 80% of patients who receive radiotherapy for abdominal and pelvic tumors suffer from intestinal injury. Furthermore, there is currently no option available to rescue radiation-induced intestinal damage.
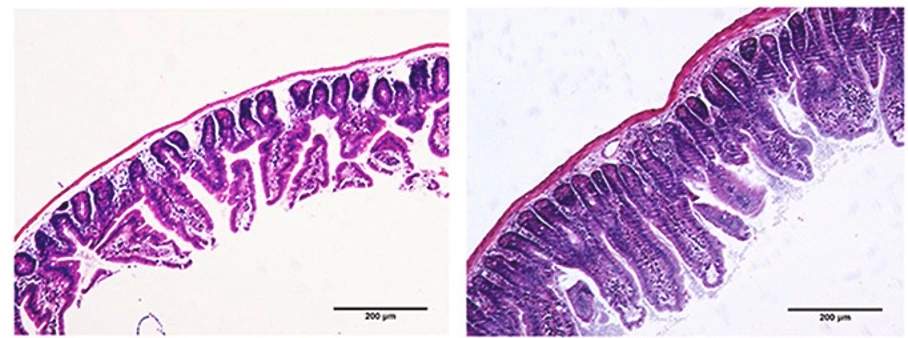
Radiation exposed intestinal wall tissue before (left) and after (right) NMN treatment.
Now, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College report in Free Radical Biology and Medicine that NMN ameliorates radiation-induced damage in mice. In mouse intestinal cells deficient in a protein called NRF2, Zhao and colleagues show that NMN reduces DNA damage and decreases ROS invoked by radiation. Treatment with NMN also protects against radiation-induced intestinal injury in mice deficient in NRF2. The promising effects of NMN were mediated by increases in sirtuin enzymes.
NMN Protects the Intestinal Wall from Radiation
Radiation kills cancer cells by producing ROS and inducing DNA damage, but it can also cause damage to surrounding cells. The NRF2 protein plays an important role in reducing ROS and DNA damage but decreases with aging. Thus, NRF2 deficiency makes elderly individuals more susceptible to radiation-induced damage. For this reason, Zhao and colleagues experimented with NRF2-deficient cells to model what occurs with aging.
Not only did NRF2-deficient intestinal cells exposed to radiation display increased levels of ROS, DNA damage, and cell death, but they also had more senescent cells — cells that progress the aging process when not eliminated. These findings suggest that radiation may trigger senescence in cancer patients. Moreover, NMN treatment reduced ROS, DNA damage, and cell death. These findings suggest that NMN can help compensate for NRF2 deficiency in intestinal cells challenged with radiation.
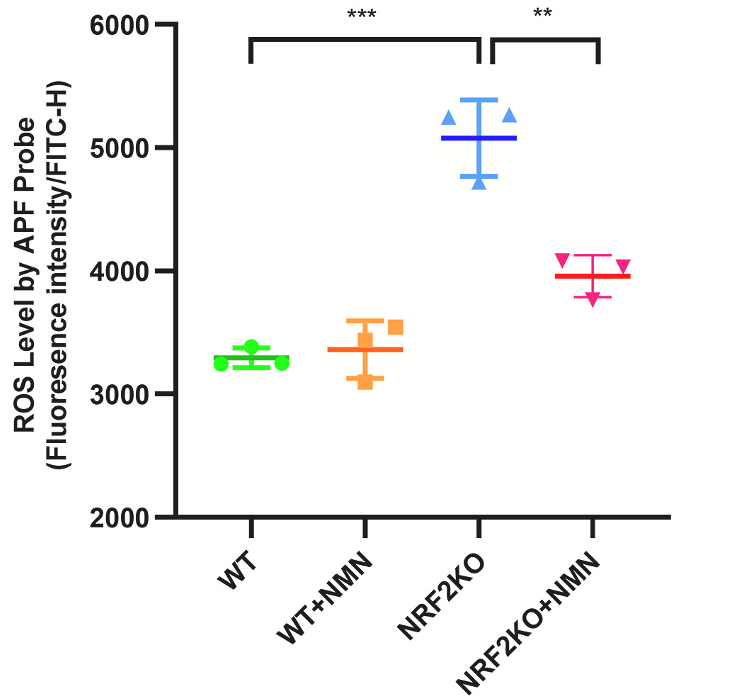
Zhao et al., 2022 | Radic. Biol. Med.)
NMN Reduces Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). When the NRF2 protein is genetically removed from mouse intestinal cells (NRF2KO), ROS levels are increased. However, treating these cells with NMN (NRF2KO+NMN) reduces ROS levels.
Sirtuins are enzymes that use NAD+ to fuel cell survival activity. Zhao and colleagues showed that NMN increased sirtuin protein levels, suggesting NMN’s effects are mediated by sirtuins. They then tested whether NMN and sirtuins protect against radiation-induced intestinal damage by feeding NRF2-deficient mice 300 mg/kg/day of NMN. The mice were then exposed to abdominal radiation.
Intestinal damage was measured by assessing several features of the intestinal wall, including villi length. Villi are outgrowths of the intestinal wall that help to increase the surface area of the intestine for nutrient absorption. While radiation exposure led to decreased villi length in untreated NRF2-deficient mice, when these mice were treated with NMN, villi length was restored. These findings show that NMN protects against radiation-induced intestinal damage in cases of low NRF2.
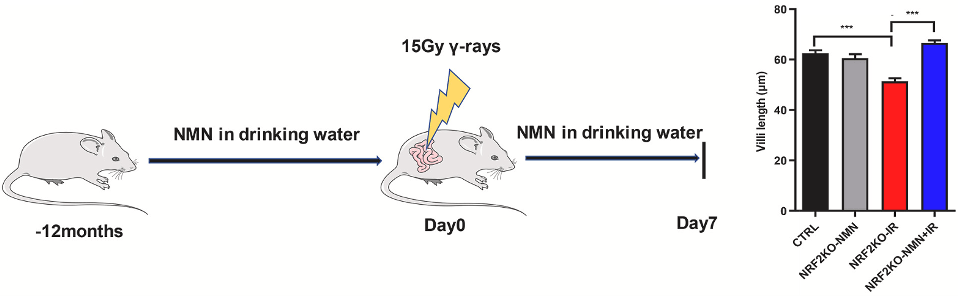
Zhao et al., 2022 | Radic. Biol. Med.)
NMN Protects Against Radiation-Induced Intestinal Damage. Compared to untreated NRF2-deficient mice (CTRL), NRF2-deficient mice exposed to ionizing radiation (NRF2KO-IR) have short villi. However, treating these mice with NMN (NRF2KO-NMN + IR) restores villi length.
Previous studies have shown that NMN promotes the function of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1). However, there exists a family of seven sirtuins, and in this study, NMN increased sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) and sirtuin 7 (SIRT7). These sirtuins seem to have antioxidant properties, as they mediate the reduction in ROS — oxidants that can cause damage to cells. Sirtuins also mediate DNA repair processes.
“Our results reveal the function of SIRT6 and SIRT7 independent of NRF2 and implicate the sophisticated network of sirtuin family [members] as regulators of different physiological or pathological states,” say the authors.
NMN Reduces Cancer Treatment Side Effects and Enhances Efficacy
Cancer treatments are far from perfect and come with long-term side effects. However, some of these side effects are prevented by NMN. For example, NMN combined with troxerutin was shown to fully protect the heart from damage caused by the chemotherapy drug doxorubicin. Now, Zhao and colleagues show that NMN can alleviate the long-term side effects of radiation therapy.
“NMN could be a promising supplement to alleviate radiation-induced intestinal injury,” state the authors.
NMN also enhances the effects of immunotherapies, the latest innovation in cancer therapy that utilizes immune cells to suppress tumor progression. For example, NMN was shown to enhance natural killer cell immunotherapy against skin and liver cancer and boosts CAR-T cell immunotherapy against blood cancer. Furthermore, the NAD+ precursor NR has also been shown to enhance immunotherapies and NRH prevents tumor regrowth after brain cancer surgery. Thus, boosting NAD+ with its precursors holds promise in conjunction with traditional cancer treatments.
Story Source
Zhao X, Zhang M, Wang J, Ji K, Wang Y, Sun X, Xu C, Wang Q, He N, Song H, Du L, Wang F, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu Q. NMN ameliorated radiation-induced damage in NRF2-deficient cell and mice via regulating SIRT6 and SIRT7. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Oct 14:S0891-5849(22)00897-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.10.267. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36252808.
Chinese scientists find that boosting NAD+ with its precursor, NMN improves the learning and memory of a mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease.
By Victor Ciardha
Highlights:
While the accumulation of a protein called beta-amyloid (Aβ) is undoubtedly involved, the underlying cause of AD is still a mystery. And as the search for a cure continues, a new study published in Biological Research has shown that NAD+, an essential molecule needed to produce the energy of all cells, may play a key role.
In the study, Hu and colleagues from the Shanghai Geriatric Institute of Chinese Medicine reveal that boosting NAD+ reverses AD defects in a mouse model for AD. The researchers treated AD mice with either NMN, an NAD+ precursor that promotes the synthesis of NAD+, or a CD38 inhibitor (antibody). As an NAD+ degrading enzyme that increases with age, CD38 is considered the primary contributor to age-related NAD+ decline. The results showed that NMN or the CD38 inhibitor improve the learning and memory of AD mice and reduces inflammation, a hallmark of aging. Furthermore, boosting NAD+ decreases the prevalence of Aβ.
Boosting NAD+ Reverses Alzheimer’s Disease Defects
Demonstrating the cognitive deficits associated with AD, Hu and colleagues showed that AD mice perform worse on learning and memory tests than aged mice without AD. However, the learning and memory of AD mice improved after treatment with NMN or the CD38 inhibitor, suggesting that boosting NAD+ could improve the cognitive deficits associated with AD.
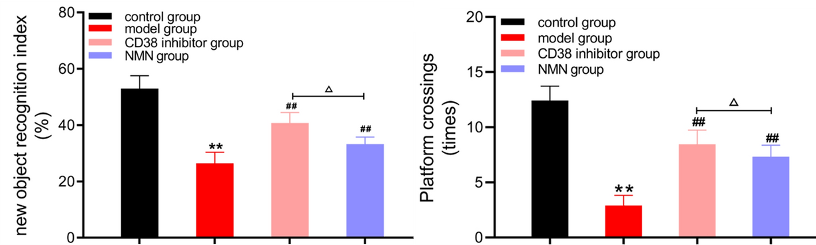
(Hu et al., 2022 | Biological Research) Learning and Memory are Improved by NMN and CD38 Inhibition. Relative to typically aged mice (black – control group), untreated AD mice (red – model group) have reduced learning and memory scores, measured by new object recognition (left) and platform crossings (right). However, AD mice treated with a CD38 inhibitor (pink – CD38 inhibitor group) or NMN (blue – NMN group) show improvements in both measurements compared to untreated AD mice.
Microglia cells are responsible for degrading harmful brain material such as excess Aβ. However, this degrading process (phagocytosis and autophagy) is slow and promotes inflammation. Thus, if microglia cannot keep up with the production of Aβ, inflammation ensues without complete Aβ removal. To exacerbate it all, Aβ can inhibit this critical function of microglia, allowing inflammation to persist, and causing progressive damage to neurons, leading to neuron cell death (neurodegeneration) and cognitive decline.
Maintaining the energy metabolism of microglia is essential for sustaining their Aβ-degrading function. NAD+ supports energy metabolism by facilitating the production of ATP, a molecule that cells use for energy. In aged microglia cells, low NAD+ and ATP make these immune cells less efficient or incapable of degrading Aβ. Thus, boosting NAD+ could increase the production of ATP, reviving the destructive power of microglia.
Hu and colleagues showed that NMN or CD38 inhibition increased the concentration of NAD+ and ATP in the brains of AD mice while reducing inflammation. These findings suggest that boosting NAD+ restores energy metabolism and reduces inflammation in AD mice, which could explain the observed improvements in learning and memory.
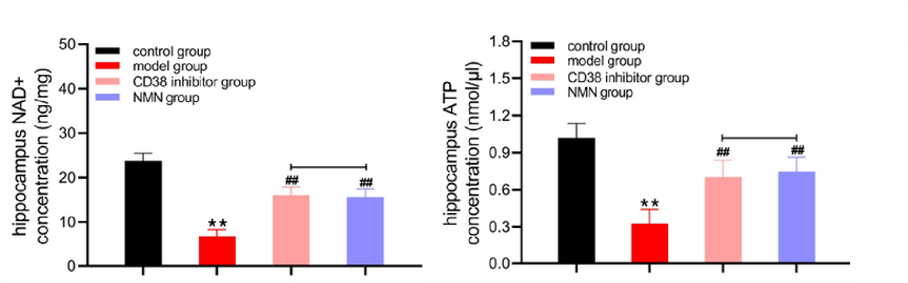
(Hu et al., 2022 | Biological Research) Energy Metabolism is Reinvigorated by NMN and CD38 Inhibition. In the hippocampus, the brain region associated with learning and memory, AD mice have lower NAD+ and ATP. Treatment with either CD38 inhibition or NMN increases NAD+ and ATP levels.
Microglia cells take different forms; in their active form, they become harmful and produce inflammatory molecules. Hu and colleagues showed that boosting NAD+ reduces microglial activation and eliminates Aβ from AD mouse brains. These findings suggest that increasing NAD+ levels restores the destructive capacity of microglia cells, enabling them to rid the brain of harmful Aβ deposits.
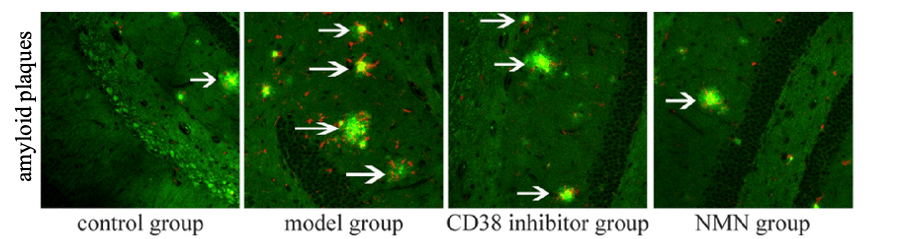
(Hu et al., 2022 | Biological Research) NMN and CD38 Inhibition Rid the Brain of Aβ. Amyloid plaques, measured with green fluorescent staining (green), were increased in untreated AD mice (model group), but reduced by a CD38 inhibitor (CD38 inhibitor group) or NMN (NMN group).
Can Boosting NAD+ Treat Alzheimer’s?
Overall, the findings of Hu and colleagues suggest that boosting NAD+ by inhibiting CD38 or supplementing with NMN revives aged microglia cells, allowing them to destroy Aβ and reduce inflammation in AD mice. This reduction in inflammation could lead to improvements in learning and memory. Another study showed that genetically removing CD38 can improve the memory of AD mice. Furthermore, boosting NAD+ with another precursor, NR, has been shown to reduce neuroinflammation, possibly leading to improved cognitive performance. Indeed, a recent study showed that reducing inflammation with a molecule called saikogenin F improves the learning and memory of AD mice.
While these animal studies make boosting NAD+ seem like a promising treatment for AD, there are not enough human studies to validate the findings. For example, a recent study showed that while NR and caffeine raise NAD+ and ATP levels in cells cultured from AD patients, it does not improve metabolic parameters. However, it is unclear from this study whether NR and caffeine could improve cognitive performance in AD patients. Thus, the effect of boosting NAD+ on cognitive performance in AD patients still needs to be tested, but the prospects seem promising.
Model and Dosage
Model: aged (30-week-old) APP/PS1 mice
Dosage: 0.093 mg/mL NMN dissolved in water and injected intraperitoneally
Story Source
Hu Y, Huang Y, Xing S, Chen C, Shen D, Chen J. Aβ promotes CD38 expression in senescent microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Res. 2022 Mar 3;55(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00379-1. PMID: 35241173; PMCID: PMC8892694.
Journal Reference
Blacher E, Dadali T, Bespalko A, Haupenthal VJ, Grimm MO, Hartmann T, Lund FE, Stein R, Levy A. Alzheimer’s disease pathology is attenuated in a CD38-deficient mouse model. Ann Neurol. 2015 Jul;78(1):88-103. doi: 10.1002/ana.24425. Epub 2015 May 25. PMID: 25893674; PMCID: PMC6929692.
Roboon J, Hattori T, Ishii H, Takarada-Iemata M, Nguyen DT, Heer CD, O’Meally D, Brenner C, Yamamoto Y, Okamoto H, Higashida H, Hori O. Inhibition of CD38 and supplementation of nicotinamide riboside ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial and astrocytic neuroinflammation by increasing NAD. J Neurochem. 2021 Jul;158(2):311-327. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15367. Epub 2021 May 9. PMID: 33871064; PMCID: PMC8282715.
Chen Z-H, Li J, Zhao X-X, et al. Saikogenin F From Bupleurum smithii Ameliorates Learning and Memory Impairment via Antiinflammation Effect in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Natural Product Communications. July 2022. doi:10.1177/1934578X221111029
Ryu WI, Shen M, Lee Y, Healy RA, Bormann MK, Cohen BM, Sonntag KC. Nicotinamide riboside and caffeine partially restore diminished NAD availability but not altered energy metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Cell. 2022 Jun 21:e13658. doi: 10.1111/acel.13658. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35730144.
A recently-published University of Toyama study from Japan reveals that a daily intake of 250 mg of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) significantly raises blood NAD+.
By Brett J. Weiss www.nmn.com
Highlights
Healthy aging has become a keynote topic as the world’s population grows older and the proportion of elderly individuals becomes larger. Known as the “silver tsunami,” the number of individuals over the age of 60 is expected to double by 2050. Accumulating research from the last 10 years or so suggests that enhancing cell energy production with NAD+ precursors, including NMN and nicotinamide riboside (NR), prevents the waning organ and tissue function associated with aging. Furthermore, scientists are seeking to confirm whether these precursors effectively increase blood concentrations of the essential molecule NAD+.
Published in Frontiers in Nutrition, Nakagawa and colleagues recently demonstrated that in healthy humans between 22 and 64 years old, NMN substantially increased blood NAD+ levels with oral usage of 250 mg per day. Blood NAD+ levels almost doubled and plateaued at approximately four weeks of usage and were sustained for the 12-week duration of the clinical trial. No negative blood measurements pertaining to blood fats, white blood cell counts, or liver function markers were observed after four weeks of NMN supplementation. No adverse effects on body weight or blood pressure were seen, either. What’s more, elevations in heart rate were strongly correlated with increased whole blood NAD+ levels, indicating that a higher heart rate facilitates the metabolism of NAD+, leading to greater NAD+ levels.
“We demonstrated that taking 250 mg of NMN every day for 12 weeks is a safe and well-tolerated practice in healthy individuals,” stated Nakagawa and colleagues in their publication. “These results suggest that the oral administration of NMN is safe and can be a practical strategy to boost NAD+ levels in humans.”
Taking NMN Nearly Doubles Blood NAD+ Levels
Nakagawa and colleagues looked at the NAD+ and NMN levels in whole blood measurements during the 12-week time course of NMN administration. The researchers found that NAD+ levels nearly doubled from over 20 µM to almost 45 µM concentrations in blood after four weeks. These blood NAD+ values plateaued to about week 12 and then expectedly dissipated after four weeks of stopping NMN supplementation. Moreover, the levels of NMN itself in blood showed no differences compared to subjects who did not receive NMN, suggesting that cells almost completely metabolize NMN from the blood. These findings show that 250 mg of NMN is easily metabolized and leads to nearly doubled blood NAD+ levels, which trend toward dissipating after four weeks.
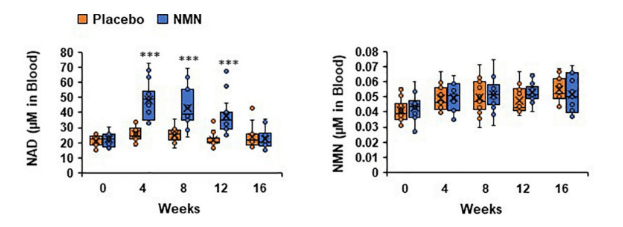
(Okabe et al., 2022 | Frontiers in Nutriton) Supplementing with NMN for 12 weeks stimulates nearly double-fold levels of blood NAD+ without increasing whole blood NMN levels. Beginning at four weeks of taking NMN orally at 250 mg per day, whole blood levels of NMN nearly double and plateau for the remainder of the treatment duration (graph on the left). Blood NMN levels remain unchanged throughout the 12-week supplementation duration and four weeks following NMN dosing cessation (week 16). These results demonstrate that supplementing humans with NMN not only nearly doubles blood NAD+ levels but also that NMN levels do not increase, showing that blood NMN may be substantially metabolized.
NMN Drives No Adverse Side Effects in Humans
NAD+ plays a vital role in thousands of biochemical reactions within cells and maintains energy levels by supporting the generation of the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of our cells. In mouse models, increasing NAD+ throughout the body protects against the age-related organ and tissue degeneration associated with diseases like cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and liver disease. To promote proper physiological function, proteins called poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) consume NAD+ to repair damaged DNA. Other proteins called Sirtuins utilize NAD+ to regulate gene function, metabolism, and the body’s stress response. All of these findings regarding NAD+ demonstrate that increasing the cellular abundance of this molecule may hold the key to promoting far healthier aging in humans. However, when it comes to boosting NAD+ in humans, safety becomes a critical factor.
To then test whether taking 250 mg/day doses of NMN drives any adverse side effects, the Japan-based research team examined a few important physiological parameters. Nakagawa and colleagues found that 12-week NMN supplementation had no effect on body weight, showing no weight gain or loss. The research team also found no significant changes in body mass index, a ratio of body weight over physical height used as a measurement of body fat. Also, blood pressure measurements remained stable during supplementation. These data suggest that no adverse physiological side effects could be attributed to taking 250 mg per day of NMN for 12 weeks.
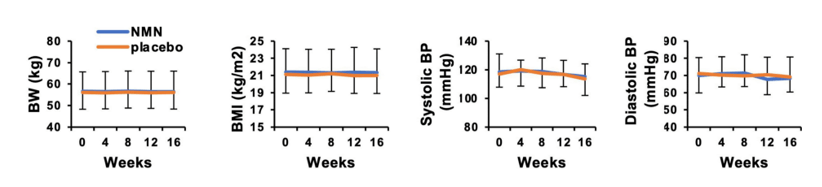
(Okabe et al., 2022 | Frontiers in Nutriton) Oral NMN supplementation with 250 mg per day for 12 weeks causes no significant changes in physiological measurements of body weight or blood pressure. Starting from the left, the graphs show that administering oral NMN causes no changes in body weight (BW), body mass index (BMI), heart pumping pressure (systolic blood pressure), or pressure from the heart filling with blood (diastolic blood pressure). These findings indicate that supplementing with NMN gives no major physiological side effects.
Nakagawa and colleagues sought to find whether pulse rate correlated with an increase in total blood NAD+ levels. They found a strong correlation (R=0.768) between blood NAD+ levels and pulse rates. For example, subjects with a pulse rate of 100 beats per minute displayed about double the blood NAD+ levels compared to those with pulse rates of about 60 beats per minute. These results support the notion that a higher heart rate drives the metabolism of NMN into NAD+.
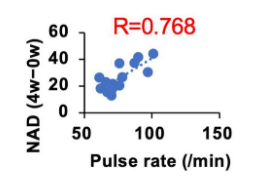
(Okabe et al., 2022 | Frontiers in Nutriton) A higher pulse rate is correlated with greater blood NAD+ levels over a four-week time course while taking 250 mg per day of NMN. Over four weeks of taking NMN, pulse rates as high as 100 beats per minute correlated with almost double the blood NAD+ levels compared to pulse rates of about 60 beats per minute. Research still does not know the exact reason or mechanism for this intriguing finding, but the possibility remains that increasing pulse rate with exercise after NMN consumption may further increase blood NAD+ levels.
Conclusive Results About NMN Will Require More Subjects and Longer Study Durations
There are several limitations to this study that necessitate further research. The current study included only 15 healthy subjects who took NMN, so future studies with more participants will be necessary to confirm the finding. While Nakagawa and colleagues show that NMN increases blood NAD+ levels, this does not necessarily mean that NAD+ levels are increased in any specific organ or tissue. Other human studies have failed to show that NMN or NR supplementation increases NAD+ levels in skeletal muscle. Therefore, future studies should also test whether administering oral NMN increases NAD+ in other organ tissues outside of the blood. In this study, the long-term effects of increasing NAD+ levels were also not tested. In order to identify any potential long-term side effects, researchers should look at human metabolic profiles following longer time courses, such as years of NMN supplementation, in healthy and non-healthy subjects.
One of the more interesting findings of this study is that higher pulse rates are correlated with increased levels of NAD+ blood availability. If true, this finding could mean that activities inducing an elevated heart rate, such as exercising, stimulate higher blood NAD+ levels.
Story Source
Okabe K, Yaku K, Uchida Y, Fukamizu Y, Sato T, Sakurai T, Tobe K, Nakagawa T. Oral Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Is Safe and Efficiently Increases Blood Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Levels in Healthy Subjects. Front Nutr. 2022 Apr 11;9:868640. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.868640. PMID: 35479740; PMCID: PMC9036060.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)-treated antitumor CAR-T cells display enhanced effectiveness to combat cancer cells and reduce tumor growth in mice.
By Brett J. Weiss www.nmn.com
Highlights
Our immune system doesn’t only seek and destroy foreign substances from outside our body, it also eliminates problematic cells internally, like cancer cells and tumor growth. However, with age our immune system becomes less efficient and internal cellular errors become more probable, leading to an increased likelihood of cancer.
In an effort to give the immune system a kick, CAR-T cell therapy has been used against malignancies, especially blood cancers, which other treatments do not effectively treat. At the same time, this treatment option is limited by poor T cell survival and lack of persistent efficacy against cancer cells. Along those lines, researchers have sought new ways to improve CAR-T cell longevity and persistent capabilities to fight against cancer.
In a non-peer reviewed preprint report, Zhong and colleagues from the Capital Medical University in Beijing China demonstrate that treating CAR-T cells with 100 µM of NMN significantly improves their efficacy and persistence to attack cancer cells. Moreover, NMN treatment enhances signs of delayed cell aging, like telomere length and reduces the buildup of dead or dying CAR-T cells. What’s more, when NMN-treated CAR-T cells were injected into mice that had experimentally-induced tumors, tumor sizes significantly diminished. These findings point to a new avenue where researchers may treat CAR-T cells with NMN to improve their viability and effectiveness to fight cancer.
NMN Treatment Enhances Cancer-Fighting Abilities
To investigate the effect of NMN on human CAR-T cell proliferation and cancer-killing capacity, CAR-T cells were treated with 100 µM NMN in the presence of NALM-6 cells in culture. NALM-6 cells are a leukemia cell line that mimic the cellular conditions of blood cancer. The China-based team found that for the NMN-treated cells, a drastic 180 times more CAR-T cells were present after 28 days of culture, compared to almost all CAR-T cells dying without NMN. Moreover, in the presence of NMN, CAR-T cells maintained their ability to kill (lyse) malignant cells longer than that of non-NMN treated CAR-T cells. These results lend credulity to the notion that NMN enhances the proliferation and tumor-killing function of CAR-T cells in culture.
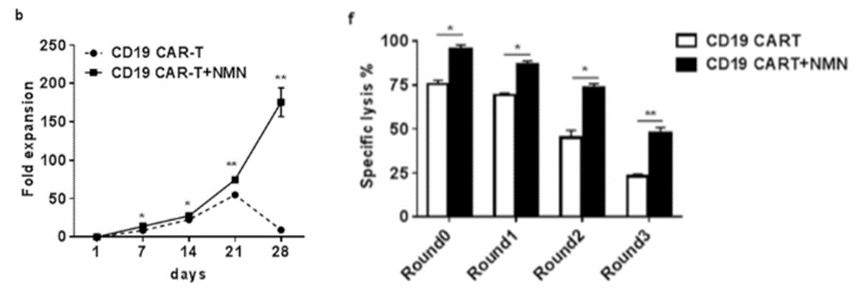
(Yu et al., 2022 | Research Square) NMN treatment dramatically enhances antitumor CAR-T cell proliferation and improves cancer attacking capabilities. Over the course of 28 days, NMN-treated CAR-T cells proliferate 180 times more than non-NMN treated CAR-T cells, which essentially die off (Figure b). CAR-T cells were treated with 100 uM of NMN four times (Round0 through Round3) over the course of 28 days. At round three (28 days), NMN-treated CAR-T cells killed (lysed) double the percentage of NALM-6 leukemia cells killed by non-NMN-treated CAR-T cells (Figure f). These findings illustrate that NMN enhances proliferation and cancer-fighting capabilities of CAR-T cells in culture.
To find whether NMN delays the aging of CAR-T cells, Zhong and colleagues tested the activity of the enzyme telomerase, which extends telomeres at the ends of chromosomes. Telomerase is a critical factor in CAR-T cell replication and overall function, and its abundance diminishes in cell division, aging, and disease.With reduced telomerase activity, CAR-T cells typically die or become aged, non-functional, and non-proliferating (senescent), leading to inhibited CAR-T function and a lack of prolonged cancer-fighting capabilities. Zhong and colleagues found that treating CAR-T cells with NMN increased telomerase activity while senescent CAR-T cell abundance substantially decreased. This finding confirms that NMN extends CAR-T cell longevity and prolongs action by promoting telomerase activity and reducing the numbers of senescent CAR-T cells in culture.
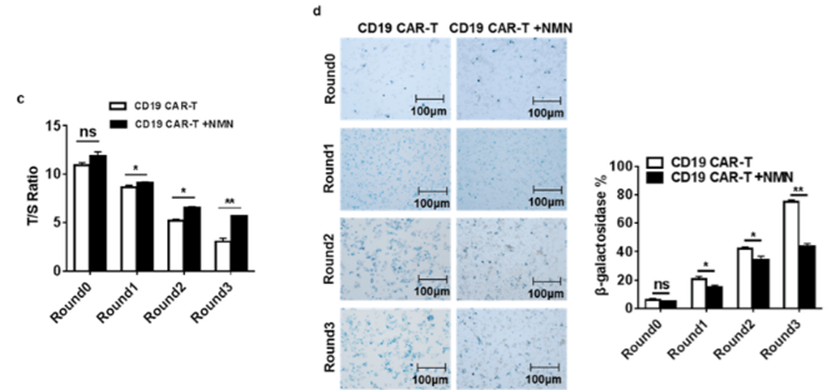
(Yu et al., 2022 | Research Square) NMN treatment significantly slows the attrition of chromosome ends (telomeres) in CAR-T cells and slows their aging. CAR-T cells were treated with 100 µM of NMN for four rounds (Round0 through Round3) over a 28-day time course, slowing down the deterioration of telomere length compared to non-treated CAR-T cells (Figure c). With NMN treatment, the numbers of senescent CAR-T cells in culture (blue dots labeled with β-galactosidase) were about half those of the non-NMN treated cells after 28 days (Figure d). These findings suggest that NMN promotes CAR-T cell longevity.
NMN-Treated CAR-T Cells Suppress Tumor Growth in Mice
Zhong and colleagues next sought to find what effects NMN-treated CAR-T cells have on tumors in mice. Mice were first injected with NALM-6 leukemia cells to generate a mouse cancer model and then injected with NMN-treated CAR-T cells. The Beijing-based team found that treatment with NMN-treated CAR-T cells promoted longer-lasting tumor suppression as shown by lower tumor volumes. These findings provide further support that NMN enhances the cancer-fighting capabilities of CAR-T cells as demonstrated in this mouse model for cancer.
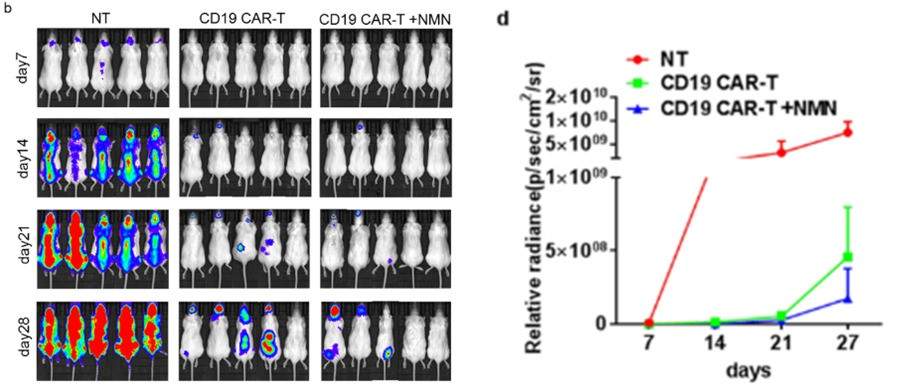
(Yu et al., 2022 | Research Square) NMN-treated CAR-T cells suppress mouse tumors. Mice were injected with human NALM-6 leukemia cells to promote tumor growth. The mice were then given no treatment (NT), CAR-T cells with no NMN (CD19 CAR-T), or NMN-treated CAR-T cells (CD19 CAR-T + NMN). After a 28-day time course, mice that received NMN-treated CD19 CAR-T cells had a lower tumor burden as shown by lower tumor radiance (figure b and d). The effects of the NMN-treated CD19 CAR-T cells were also longer lasting as illustrated by the lower tumor burden after 28 days.
NMN Stimulates the Longevity-Associated Sirt1 Gene
To find out what genes NMN stimulates, Zhong and colleagues performed gene activity analyses and found that NMN promotes the activation of the Sirt1 gene, associated with cell longevity. In NMN-treated CAR-T cells, increased Sirt1 activity was also linked with decreased activation of cell death and inflammation-associated genes. Since Sirt1 has a presumed role in suppressing the activation of cell death-associated genes, these findings provide some clues for the cell mechanism through which NMN promotes CAR-T antitumor efficacy.
Identifying Which Precise Cell Mechanisms NMN Stimulates
“In this study, we found that NMN can increase cell rejuvenation and cell proliferation by upregulating Sirt1 and provide us with great confidence NMN can enhance CD19 CAR-T cell longevity and anti-tumor efficiency,” said Zhong and colleagues in their publication.
The findings of the study highlight the potential clinical application of NMN for CAR-T cell human cancer immunotherapy. With NMN application, human CAR-T cells were more viable and had better capabilities to kill cancer cells. These findings also applied to a mouse cancer model, where injections of NMN-treated CAR-T cells reduced tumor growth, illustrating that NMN may be the key to enhance CAR-T therapy.
Future studies need to elucidate the precise cellular mechanisms by which NMN promotes CAR-T viability, longevity, and cancer-fighting abilities. A more detailed look at NMN’s effects on cells will allow researchers to pinpoint other pathways that NMN influences. In doing so, we may gain further insight into improving CAR-T cell function to fight against cancer.
This study provides insights into how NMN helps rejuvenate the immune system by jump starting CAR-T cells. Since the immune system declines with aging, it is possible that NMN could be used as a preventative measure against cancer growth.
Story Source
Zhen Yu, Shuai Tong, Can Zhang et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide enhances the efficacy and persistence of CD19 CAR-T cells via NAD + –Sirt1 axis, 19 April 2022, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square [https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1483519/v1]