Treating human cells with NMN triples NAD+ levels and increases the activity of AMPK — an enzyme that turns on sugar and fat metabolism in response to low energy.
By Brett J. Weiss www.nmn.com
Highlights
Increasing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels has promising anti-aging capabilities due to its fundamental role in cellular health. Likewise, AMPK, which is usually activated in response to low energy levels (including caloric restriction) is a fundamental molecule that promotes processes associated with longevity. Research has shown that taking the supplement nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) nearly doubles NAD+ in humans. Improvements in metabolic parameters like insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women and muscle oxygen utilization in long-distance runners have also been correlated with increasing NAD+ levels. Yet, dissecting a more precise cellular mechanism by which increasing NAD+ levels confer these benefits has yet to be done.
Published in the Journal of Biomedical Research and Environmental Sciences, Yamamoto and colleagues from Wellness-One Co., Ltd in Japan demonstrate that treating human MCF-7 breast cancer cells with 1 mg/mL NMN in culture raises AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activity over 1,200%. What’s more, NMN treatment raised intracellular NAD+ levels three-fold. These findings suggest that by increasing NAD+ levels, NMN could boost the longevity-associated processes activated by AMPK, including enhanced mitochondrial health and autophagy — the cellular debris disposal system. This study also provides more evidence that supplementing with NAD+ precursors like NMN may drive cell energy production to alleviate faltering energy levels during aging.
NMN Boosts AMPK Activity 12-Fold and Raises NAD+ Levels
To test the effects of administering NMN on AMPK activity, Yamamoto and colleagues treated MCF-7 human breast cancer cells with 1 mg/kg in culture and measured AMPK activity. Over the course of 24 hours, the researchers found that AMPK activity increased an astounding 1230.5% after one hour, 506.5% after 12 hours, and 849.2% after 24 hours compared to cells without treatment. These findings suggest that NMN treatment has a profound effect on amplifying AMPK activity, suggesting the promotion of processes like mitochondrial production and autophagy, both shown to have anti-aging effects.
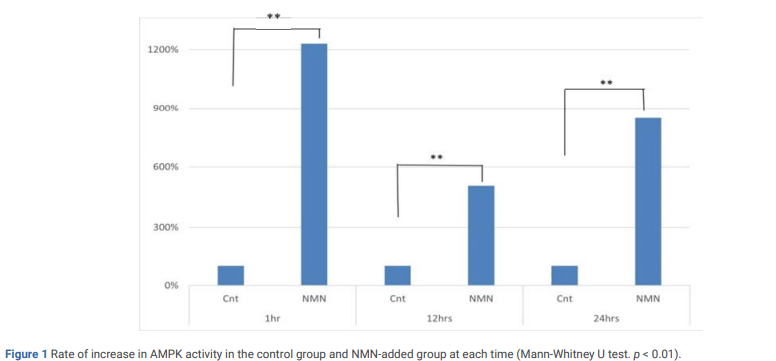
(Kawakami et al., 2022 | Journal of Biomedical Research & Environmental Sciences) NMN dramatically increases the activity of the metabolic health-promoting protein AMPK. After treating MDF-7 human breast cancer cells with 1 mg/mL NMN, AMPK activity increased over 1,200% after one hour, over 500% after 12 hours, and approximately 850% after 24 hours. These results highlight the impact of NMN treatment on increasing AMPK activity.
AMPK has recently garnered substantial attention in aging research. For example, AMPK has been found to regulate cellular energy balance, protect mitochondrial function, and facilitate a cell debris-cleaning process called autophagy. Perhaps most interestingly, by enhancing mitochondrial function, AMPK acts as a molecular energy switch for the production of the cell energy molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) when ATP levels fall. Faltering AMPK activity with age has been linked to reduced energy levels in older adults. Therefore, increasing AMPK activity could mitigate age-related disease and promote longevity.
Yamamoto and colleagues tested the effects of treating cancer cells with NMN on intracellular NAD+ levels. The research team found that NMN more than tripled NAD+ levels within the MCF-7 cells. These results recapitulate previous findings showing that NMN effectively boosts NAD+ levels by substantial amounts in human cells.
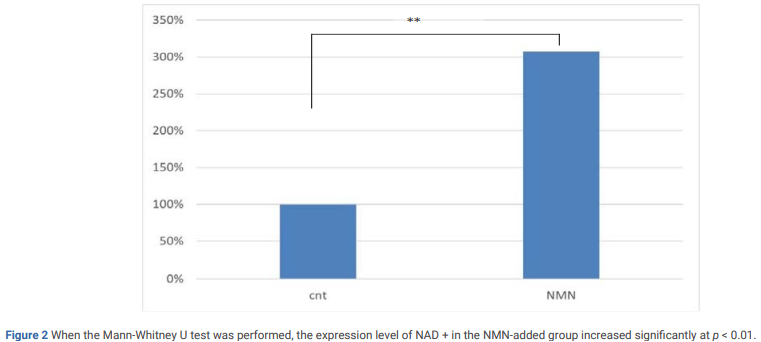
(Kawakami et al., 2022 | Journal of Biomedical Research & Environmental Sciences) NMN triples intracellular NAD+ levels in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Human MCF-7 breast cancer cells were treated with 1 mg/mL NMN in culture. Light absorbance was then measured to detect the presence of NAD+. Compared to non-treated cells, those that received NMN had more than triple the NAD+ concentrations within them. These results support that NMN treatment substantially increases NAD+ levels in human cells.
Does Testing Cancer Cells Recapitulate NMN’s Effects on Healthy Cells?
By enhancing the activity of the cell energy-regulating AMPK, NMN may promote cellular rejuvenation as breast cancer cells age. Possibly the biggest issue with the study, though, was that Yamamoto and colleagues used the MCF-7 breast cancer cell lineage that may have already had low AMPK activation and faltering NAD+ levels. There are numerous alternative cell lines that do not come from diseased tissues like breast cancer that Yamamoto and colleagues could have used, such as vascular cells (endothelial cells). The use of the breast cancer cells may be seen as a major limitation of the study since little is known about how diseased tissue like cancer affects AMPK activity and NAD+ levels.
Analyzing NMN’s Impact on Blood ATP Levels in HumansFuture studies examining the efficacy of NMN against aging could look at blood plasma ATP levels to find out whether taking NMN boosts cell energy. The recommended dose of NMN lies somewhere between 250 mg to 500 mg per day, so a dose-dependency analysis could test the effects of different daily doses of NMN. This experiment could span over the course of a few months to find out whether NMN not only potentially boosts AMPK activity and NAD+ levels but also results in higher ATP production.
Story Source
Kawakami S, Fukuzawa Y, Ichikawa H, Sato T, Ide T, Maeda Y, Yamamoto T. NMN “Nicotinamide Mononucleotide” Activates Intracellular Energy and Approaches the Prevention and Improvement of Aging. J Biomed Res Environ Sci. 2022 May 21; 3(5): 560-565. doi: 10.37871/jbres1480, Article ID: JBRES1480, Available at: https://www.jelsciences.com/ articles/jbres1480.pdf
The anti-aging compounds NMN, metformin, and rapamycin prevent brain damage and alleviate memory deficiencies in a rat model for age-related cognitive impairment.
By Brett J. Weiss www.nmn.com
Highlights
While Alzhimer’s gets all the press coverage, not many know about the second leading cause of dementia, VCI. VCI comes from obstructed blood flow to the brain from diseases like heart complications or disorders such as high cholesterol. This leads to cognitive impairment – where people lose their abilities to take care of themselves due to deteriorating brain function. Despite its prevalence, like Alzheimer’s, no therapy currently exists to delay or prevent VCI.
Published in Frontiers in Neurology, Jin and colleagues from the University of North Texas showed that pretreating rats with nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), metformin, or rapamycin before experimentally reducing blood flow to the brain to mimic VCI attenuates cognitive impairment. The research team also showed that treatment with any of the three anti-aging molecules reduces brain lesions in VCI rats. Moreover, the occurrence of myelin degradation) declines in rats treated with any of the anti-aging compounds. These findings provide exciting evidence that treatment with NMN, metformin, or rapamycin may provide a means to prevent cognitive decline associated with VCI.
Anti-Aging Compounds Preserve Cognition After Reduced Blood Flow to the Brain
To test the effects of NMN, metformin, and rapamycin on VCI, Jin and colleagues pretreated rats with one of the three anti-aging compounds for 14 days prior to experimentally obstructing blood flow to their brains to model VCI. To determine whether the anti-aging compounds improve the cognitive deficits associated with VCI, the researchers measured learning and memory with the Morris water maze. In the water maze, the rats were trained during four trials to find a submerged platform that would allow them to escape from swimming. Rats that were pretreated with any of the anti-aging compounds spent significantly longer periods in the area that contained the platform, indicating improved memory of the platform’s location. These findings illustrate that NMN, metformin, or rapamycin can restore cognition with obstructed blood flow to the brain, similar to VCI.
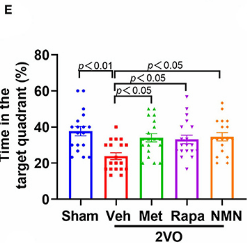
(Yu et al., 2022 | Frontiers in Neurology) NMN, metformin, and rapamycin prevent cognitive impairment following reduced blood flow to the brain. Healthy (Sham) rats and rats that underwent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion, mimicking VCI (2VO), were subjected to the Morris water maze. In the untreated 2VO rats (Veh), the time spent searching the target area for the platform was significantly reduced, indicating impaired memory. Treatment of the rats for 14 days with NMN, metformin, or rapamycin prior to reducing blood flow to the brain prevented this loss of ability to memorize platform area.
To dig into the cell mechanism by which the three compounds exert their cognition-preserving effects, Jin and colleagues looked at the abundance of brain lesions. The researchers found that the treatments more than halved the abundance of lesions. Since these lesions are areas of damage to the brain, reducing their prevalence indicates a preservation of healthy functioning brain tissue, allowing for enhanced cognition.
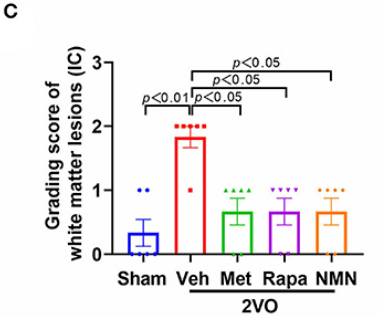
(Yu et al., 2022 | Frontiers in Neurology) NMN, metformin, and rapamycin prevent brain lesions. Sham rats had far less lesions in the areas of the brain that have the most axons (white matter) compared to untreated 2VO rats. Treatment with NMN, metformin, or rapamycin cut the number of white matter lesions present in half, indicating that the anti-aging compounds prevent this form of brain damage.
Jin and colleagues next sought to find how the anti-aging compounds reduced white matter lesions by examining the fatty tissue (myelin) that composes it. Myelin wraps around the axons of neurons allowing for electrical signals to travel at incredibly fast speeds, essentially making the brain fire quicker. They found that rats treated with the three anti-aging molecules underwent significantly less myelin degradation. These results demonstrate that by reducing myelin degradation, white matter is preserved, which improves brain function, and ultimately, cognition.
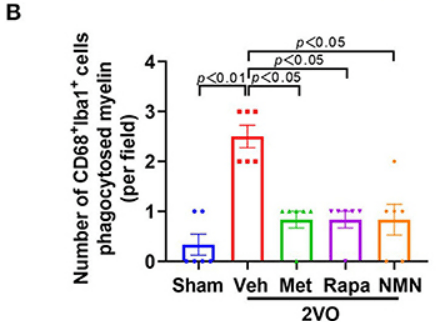
(Yu et al., 2022 | Frontiers in Neurology) NMN, metformin, and rapamycin prevent myelin degradation. The number of brain immune cells called microglia (CD68+Iba1+) cells that degraded (phagocytosed) myelin were quantified. Untreated 2VO rats had dramatically increased phagocytosed myelin compared to Sham rats. Metformin, rapamycin, and NMN more than cut in half the number of microglia cells that phagocytosed myelin, indicating that the three anti-aging molecules alleviate myelin degradation by microglia.
NMN, Metformin, and Rapamycin Converge on Similar Pathways to Suppress the Elimination of Myelin
The question of what cellular effects NMN, metformin, and rapamycin exert on brain tissue with reduced blood flow has yet to be definitively determined. Previous research indicates that rapamycin inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein from putting microglia cells into degradation mode. In the same regard, metformin stimulates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) proteins that suppress mTOR activity to exert similar effects. NMN stimulates Sirtuin1 proteins that activate AMPK to inhibit the activation of mTOR and then suppress microglia activation. For these reasons, it appears that all three anti-aging compounds converge on similar pathways to inhibit the degradation of healthy myelin under conditions that mimic VCI.
Since none of the three compounds provide more benefit than the others, a cost analysis is suitable to determine which of the three is most cost effective. Metformin costs roughly $13.72 for a month’s supply, whereas rapamycin costs nearly $100 for a month’s supply, while NMN costs around $50 for a month’s supply. While rapamycin and metformin both inhibit mTOR, metformin has the added benefit of regulating glucose metabolism, as it is normally prescribed as a type 2 diabetes medication. Compared to rapamycin and metformin, NMN exerts a broader range of benefits by stimulating sirtuin proteins to combat harmful cell oxidative stress, while also activating the AMPK protein to promote mitochondrial function and suppress mTOR.
Model and Dosage
Model: Sprague-Dawley rats
Dosage: 100 mg/kg injection of NMN, 100 mg/kg injection of metformin, .25 mg/kg injection of rapamycin
Story Source
Yu M, Zheng X, Cheng F, Shao B, Zhuge Q, Jin K. Metformin, Rapamycin, or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Pretreatment Attenuate Cognitive Impairment After Cerebral Hypoperfusion by Inhibiting Microglial Phagocytosis. Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 13;13:903565. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.903565. PMID: 35769369; PMCID: PMC9234123.
Chinese scientists find that NMN restores the age-related deterioration of the intestinal wall by boosting natural antioxidant defenses and reducing inflammation in older mice.
By Victor Ciardha www.nmn.com
Highlights:
Our intestines not only absorb the nutrients necessary to sustain life but also act as a protective barrier from the outside world. When this barrier is disrupted, harmful molecules like pathogens can sneak into our bloodstream and wreak havoc on the rest of our organs. Research suggests that this barrier becomes compromised with aging. However, a new study published in Food & Function shows that nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) can help.
Researchers from the Jiangxi Academy of Sciences in China report that NMN, a molecule capable of boosting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), protects against age-related intestinal dysfunction. Ru and colleagues show that NMN boosts NAD+ and restores intestinal wall structure in older mice. They also show that NMN increases genes associated with gut barrier integrity. Additionally, the results suggest that NMN works by reducing inflammation and boosting natural (endogenous) antioxidants.
NMN Rebuilds and Fortifies the Intestinal Lining of Old Mice
Our intestinal lining is far from smooth, consisting of projections called villi. These tiny gut wall folds increase the surface area of our intestine to the size of a tennis court, maximizing nutrient absorption. Ru and colleagues found that putting NMN in the drinking water of old mice increases the height of their villi, suggesting improved nutrient absorption. Furthermore, NMN was shown to increase NAD+ levels in the same area of the small intestine called the jejunum.
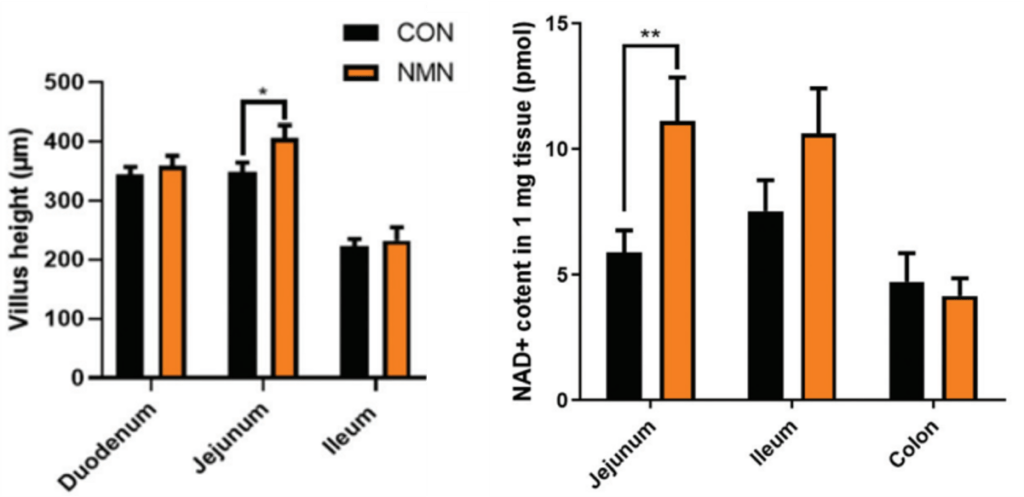
(Ru et al., 2022 | Food & Function) Boosting NAD+ with NMN Restores Intestinal Wall Structure in Old Mice. In a portion of the small intestine called the jejunum, oral NMN treatment increases villus height (left) and raises NAD+ levels (right).
The cells that make up our intestinal lining have gaps between them that, if too wide, can allow large harmful molecules into our bloodstream. These gaps can be narrowed by specific proteins at choke points called tight junctions (see the main image). Ru and colleagues found that NMN increases the activation of the genes associated with these proteins in older mice, suggesting that NMN reduces gut wall permeability to harmful molecules.
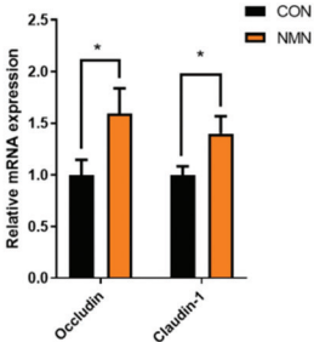
(Ru et al., 2022 | Food & Function) NMN Elevates Gut Barrier Genes in Old Mice. NMN increases the activation of genes associated with gut barrier integrity (Occludin and Claudin-1).
To determine how NMN could be reversing intestinal aging, Ru and colleagues measured genes associated with natural antioxidants and inflammation. They found that NMN increases the activation of genes associated with antioxidants (such as SOD2 and Nrf2) and decreases genes associated with inflammation. Antioxidants are capable of quelling harmful free radicals called reactive oxygen species (ROS), which contribute largely to inflammation and the organ and tissue dysfunction associated with aging.
Furthermore, NMN increases the activation of sirtuins (Sirt3 and Sirt6) — enzymes that use NAD+ as fuel, associated with improving antioxidant capacity and reducing inflammation. These findings suggest that NMN reverses intestinal aging by boosting antioxidants and mitigating inflammation through sirtuin activation.
Can NMN Prevent Multiple Diseases?
In addition to this study, NMN has been shown to protect the intestinal tract, rejuvenate intestinal stem cells, and rescue colon degeneration in older rodents. Another NAD+ precursor, nicotinamide riboside (NR) has been shown to improve intestinal lining function and also rejuvenate intestinal stem cells. These studies suggest that boosting NAD+, a molecule that declines with aging and is thought to underlie age-related conditions like neurodegeneration, heart disease, and obesity, may also underlie intestinal aging. Since leaky gut has been associated with liver disease and Alzheimer’s disease, it’s possible that boosting NAD+ with NMN can contribute to preventing or mitigating these diseases and other diseases by reversing intestinal aging as well.
Model and Dosage
Model: male C57BL/6J mice (age: 16 months)
Dosage: 500 mg/L of NMN in drinking water
Story Source
Ru M, Wang W, Zhai Z, Wang R, Li Y, Liang J, Kothari D, Niu K, Wu X. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation protects the intestinal function in aging mice and D-galactose induced senescent cells. Food Funct. 2022 Jul 18;13(14):7507-7519. doi: 10.1039/d2fo00525e. PMID: 35678708.
Journal Reference
Untersmayr E, Brandt A, Koidl L, Bergheim I. The Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction as Driving Factor of Inflammaging. Nutrients. 2022 Feb 23;14(5):949. doi: 10.3390/nu14050949. PMID: 35267924; PMCID: PMC8912763.
Researchers show NMN-boosted immune cells significantly prolong the lifespan of mice by suppressing tumors.
By Victor Ciardha www.nmn.com
Highlights:
The true assassins of our immune system, NK cells, are capable of destroying virus-infected and cancer cells directly. However, to kill off the bad cells, NK cells require lots of energy. Without enough energy, NK cells can become impaired, leading to unchecked tumor growth. Now, researchers at Shandong University may have found a way to restore this energy.
As reported in Hepatology,nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) precursor nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) invigorates the anti-tumor capabilities of NK cells. Guo and colleagues show that NMN-treated NK cells increase the lifespan of mice modeling liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma) by nearly 3-fold while reducing tumor growth. Furthermore, they show that NMN decreases tumor size in mice modeling skin cancer (melanoma).
NMN Puts Cancer Killing Cells into Overdrive
To model liver cancer in mice, Guo and colleagues injected extremely immunodeficient mice with liver cancer cells to induce tumor growth. To give NK cells a boost of energy and experiment with NK cell-based cancer therapy, the China-based researchers supplemented NK cells with NMN. By injecting the cancerous mice with NMN-treated NK cells, the researchers saw significant improvements in the overall survival of the tumor-bearing mice.
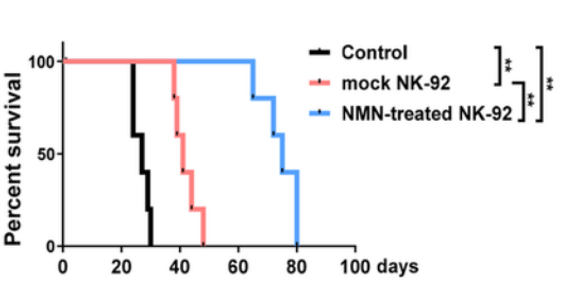
(Guo et al., 2022 | Hepatology) NMN-Treated NK Cells Increase Lifespan. Immunodeficient mice injected with liver cancer cells (black) live longer when injected with NK cells (red) and live even longer when the NK cells are treated with NMN (blue).
NAD+ is an essential molecule that mediates the production of cellular energy (ATP). By treating NK cells with NMN, NAD+ levels are increased, allowing for the production of more cellular energy. Armed with sufficient fuel, NK cells can more efficiently kill tumor cells and suppress tumor growth.
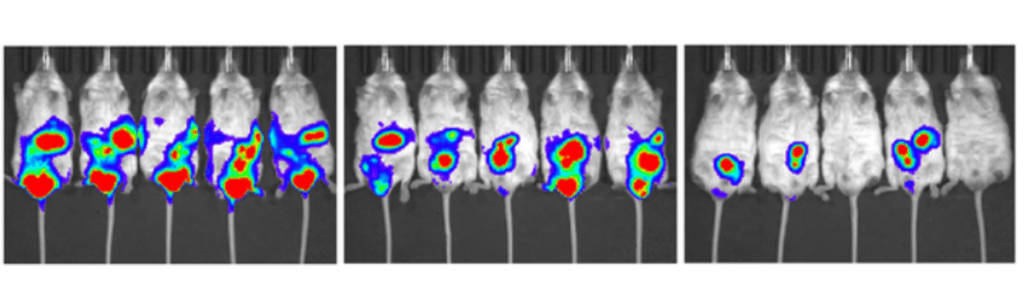
(Guo et al., 2022 | Hepatology) NMN-Treated NK Cells Suppress Liver Tumor Growth. Immunodeficient mice injected with liver cancer cells (control) have less tumor growth (measured by fluorescing tumors) when injected with NK cells (mock NK-92), and even less tumor growth when the NK cells are treated with NMN (NMN-treated NK-92).
In another cancer model, Guo and colleagues injected skin cancer cells underneath the skin of mice. These mice were then injected with NMN-treated NK cells, their tumors were subsequently harvested for measurement. It was found that NMN-treated NK cells reduce tumor size more effectively than untreated NK cells. Taken together, these findings suggest that, compared to untreated NK cells, NMN-treated NK cells can more efficiently suppress tumor growth for multiple types of cancer.

(Guo et al., 2022 | Hepatology) NMN-Treated NK Cells Suppress Skin Tumor Growth. Mice modeling skin cancer have smaller tumors when injected with NMN-treated NK cells compared to untreated NK cells (mock NK).
Is NMN Key in Immune Cell Cancer Therapy?
Immunotherapy — stimulating the immune system to fight cancer — is an emerging alternative to chemotherapy — using chemicals to fight cancer. Furthermore, NK cells are on the frontier of immunotherapeutic options, owing to their safety profile. However, in the body, NK cell efficiency is hindered by factors surrounding the tumor environment (tumor microenvironment). The findings of Guo and colleagues suggest that NMN can mitigate this hindrance. Additionally, a previous study showed that NMN enhances NK cell efficiency as well, supporting this idea. Thus, treating NK cells with NMN may solve many of the efficiency problems associated with NK cell immunotherapy.
In addition to destroying virus-infected and cancer cells, NK cells have been shown to destroy senescent cells, an effect that is enhanced by the neurotransmitter dopamine. Senescent cells are cells that can no longer divide but secrete pro-inflammatory molecules that can damage tissue. Senescent cells accumulate with aging and the inflammation they cause is thought to underly many age-related diseases. Therefore, NK cells could potentially be used to slow aging by targeting senescent cells, an effect that could apparently be enhanced by NMN (and dopamine).
Story Source
Guo X, Tan S, Wang T, Sun R, Li S, Tian P, Li M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Dong Z, Yan L, Yue X, Wu Z, Li C, Yamagata K, Gao L, Ma C, Li T, Liang X. NAD+ salvage governs mitochondrial metabolism, invigorating natural killer cell antitumor immunity. Hepatology. 2022 Jul 11. doi: 10.1002/hep.32658. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35815363.
Journal Reference
Brauning A, Rae M, Zhu G, Fulton E, Admasu TD, Stolzing A, Sharma A. Aging of the Immune System: Focus on Natural Killer Cells Phenotype and Functions. Cells. 2022 Mar 17;11(6):1017. doi: 10.3390/cells11061017. PMID: 35326467; PMCID: PMC8947539.
Liu, S, Nguyen, K, Park, D, Wong, N, Wang, A, Zhou, Y. Harnessing natural killer cells to develop next-generation cellular immunotherapy. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2022; 1- 11. doi:10.1002/cdt3.40
Wuhan University scientists show that NMN prevents severe skin damage and reduces harmful molecules called reactive oxygen species in mice.
By Victor Ciardha www.nmn.com
Highlights:
Our skin is an external barrier full of immune cells that guard our internal organs against pathogens. Like most immune cells, when skin immune cells malfunction, they promote inflammation. Such is the case with eczema (atopic dermatitis), a skin disease characterized by excessive inflammation. Due to age-related immune system decline and body-wide inflammation, we become more susceptible to eczema as we age. Now, researchers from Wuhan University in China may have found a potential treatment for eczema in nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).
As reported in International Immunopharmacology, NMN, a molecule capable of raising cellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels, may improve the inflammatory skin disease eczema. Gao and colleagues show that topical application of NMN prevents eczema-like symptoms, including skin lesions, itching, rash, and water loss in mice by blocking ROS. Since eczema and normal skin aging share common symptoms, these findings suggest that topical NMN can treat eczema and age-related skin inflammation.
NMN Prevents Inflammation-Induced Skin Damage
Gao and colleagues chemically induced skin inflammation in mice to establish an eczema mouse model. Untreated eczema model mice displayed severe skin lesions, itching, rash, and scales. Treating these mice by topical application of NMN markedly reduced these symptoms.
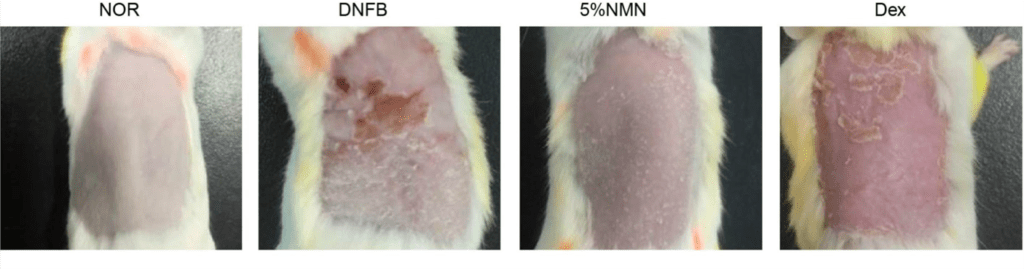
(Gao et al., 2022 | International Immunopharmacology) NMN Prevents Symptoms of Severe Skin Damage. A chemical called 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) induced eczema-like skin damage. 5% NMN prevented much of this skin damage and almost restored the skin to normal (NOR), at least more so than a known anti-inflammatory steroid medication called Dexamethasone (Dex).
Normal skin aging and eczema share several cellular processes and skin symptoms, including excessive ROS and water loss. ROS are a class of highly reactive oxygen molecules that can directly damage cells if not neutralized by antioxidants. ROS can damage the cells that form the skin’s protective barrier, fostering inflammation.
The Wuhan researchers showed that NMN reduces ROS and inflammatory molecules while increasing natural (endogenous) antioxidant levels in eczema model mice. NMN treatment also increases proteins involved in skin barrier function. Furthermore, NMN treatment reduces skin water loss, a common symptom of aging skin that contributes to dryness. These findings suggest that NMN can not only reverse aspects of eczema but also normal skin aging.
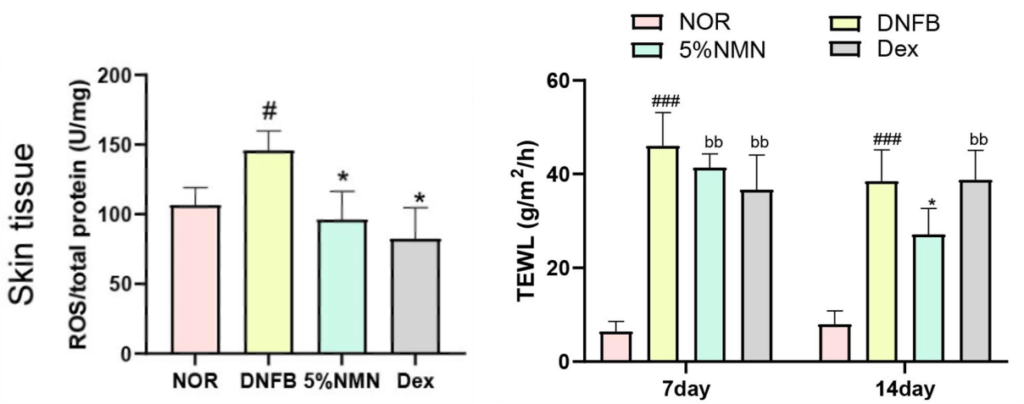
(Gao et al., 2022 | International Immunopharmacology) NMN Subdues Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Limits Water Loss. 5% NMN prevents the increase in ROS and skin water loss (TEWL) caused by 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB)-induced skin damage, more so than Dexamethasone (Dex) after 14 days of application.
NAD+ is an essential molecule that mediates the production of energy and fuels enzymes with critical cellular functions like DNA repair. Cells utilize NMN to synthesize NAD+, thus increasing its concentration levels. Gao and colleagues showed that NMN could reduce ROS, suggesting that NAD+ can alleviate oxidative stress — the damage caused to cells by excessive ROS.
Can NMN Reverse Skin Aging?
Skin aging, associated with excessive ROS and oxidative stress, is accelerated by environmental factors like ultraviolet (UV) radiation and air pollution. Therefore, treatments that limit oxidative stress can hypothetically slow down or prevent skin aging. Animal studies suggest NMN could slow accelerated skin aging by protecting against UV radiation and intestinal bacteria dysfunction. NMN also protects skin cells from particulate matter, microscopic particles often contained within polluted air. Notably, these and other studies show that NMN acts by limiting ROS and oxidative stress, suggesting that NMN is targeting one of the underlying causes of skin aging. However, there is a lack of human studies showing that NMN affects skin aging.
Model and Dosage
Model: female Kunming mice
Dosage: 5% NMN dissolved in acetone and oil applied topically to the skin
Story Source
Gao JF, Tang L, Luo F, Zhang YY, Chen L, Ding H, Meng ZD. Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in mice by blocking activation of ROS-mediated JAK2/STAT5 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108812. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108812. Epub 2022 May 6. PMID: 35533554.
Journal Reference
Bocheva GS, Slominski RM, Slominski AT. Immunological Aspects of Skin Aging in Atopic Dermatitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 27;22(11):5729. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115729. PMID: 34072076; PMCID: PMC8198400.
NMN alleviates retina damage, drops DNA damage by 50%, and eliminates senescent (aged) cells in age-related macular degeneration models.
By Victor Ciardha www.nmn.com
Highlights:
Our ability to visualize the fine details of our surroundings depends on a tiny patch of specialized neurons (photoreceptors) called the macula. With age, this region of the retina degenerates as our vision blurs, manifesting in a disease called macular degeneration. Now, scientists from Tongji University in China show that senescent cells — one of the hallmarks of aging — may contribute to macular degeneration.
As reported in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, Ren and colleagues exposed human retina cells to a chemical called sodium iodate to establish a model for macular degeneration. They found that the experimentally-induced degenerated retina cells had increased levels of senescence, DNA damage, and harmful molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS), all of which were reversed by treatment with nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). Furthermore, similar results were shown in mice, along with improvements in retina structure upon NMN treatment.
NMN Reduces Retina Damage
The retina is a layer of cells coating the back of the eye, vital for vision. Sodium iodate (NaIO3) is widely used to study age-related macular degeneration because it causes retinal degeneration. Upon exposure to NaIO3,Ren and colleagues showed that human retina cells displayed common characteristics of age-related retinal degeneration, including increased senescent cells, DNA damage, and excessive levels of ROS. By treating the degenerated retina cells with NMN, the percentage of senescent cells dropped, DNA damage was reduced by 50%, and ROS levels were suppressed.
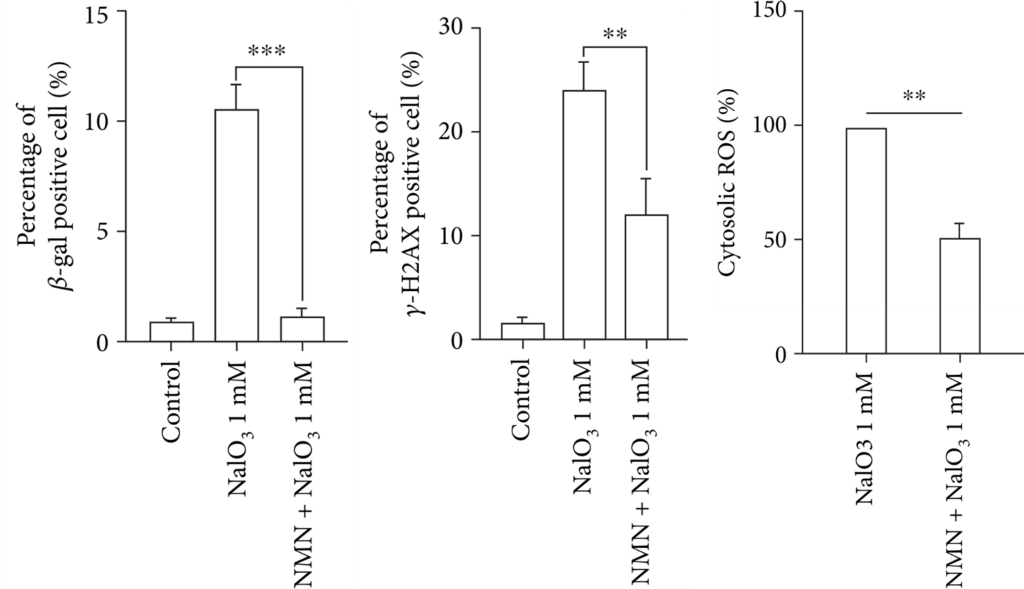
(Ren et al., 2022 | Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev.) NMN Reduces Senescence in Degenerated Human Retina Cells. Relative to normal (control) retina cells, degenerated retina cells (NaIO3 1 mM) have increased senescent cells (β-gal), DNA damage (γ-H2AX), and reactive oxygen species (cytosolic ROS), all of which are lowered by NMN (NMN + NaIO3 1 mM).
One of the hallmarks of aging is a phenomenon known as senescence, whereby normal cells become senescent in response to cellular stressors like DNA damage and excessive ROS. Excessive accumulation of senescent cells stimulates inflammation and promotes the onset of multiple age-related diseases, including macular degeneration.
To paint a more physiological picture of NMN’s effect on retinal degeneration, Ren and colleagues injected mice with NaIO3 and examined their retinas. They found that NaIO3 induced structural changes in the mouse retinas and increased senescence. However, treating the NaIO3-exposed mice with NMN mitigated the structural changes and prevented the propagation of senescent cells.
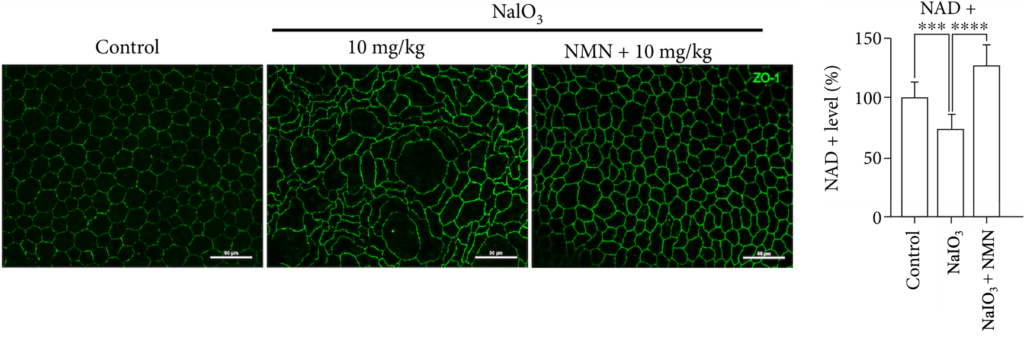
(Ren et al., 2022 | Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev.) NMN Prevents Degenerated Mouse Retina Structural Changes. Staining of proteins (green, ZO-1) in the retina shows that NaIO3 (10 mg/kg) induces structural alterations relative to normal retinas (control), which is partially reversed by NMN (NMN + 10 mg/kg). NMN also restores NAD+ levels.
The findings of Ren and colleagues suggest that NMN can reverse aspects of retinal degeneration by boosting nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). NAD+ is an important molecule involved in energy metabolism, known to fuel enzymes capable of repairing DNA and reducing ROS. NAD+ content decreases with aging in various tissues including the retina. However, the Shanghai-based researchers showed that NAD+ levels were restored with NMN in their mouse model for macular degeneration.
Can NMN Prevent Age-Related Blindness?
According to the National Eye Institute, macular degeneration can potentially lead to partial blindness. However, by slowing down the degeneration of the retina with supplements, it may be possible to prevent vision acuity loss. These supplements include vitamins and minerals like zinc, vitamin E, and vitamin C. Now, can NMN be added to this list?
NMN has previously been shown to mitigate macular degeneration and protect against retinal detachment in animal models. Additionally, an enzyme important for NAD+ synthesis is depleted in degenerated rodent retinas and grape seed extract has been shown to reverse retina aging by activating another NAD+-related enzyme in mice. This means that the enzymes necessary to generate NAD+ seem to be lost during retinal aging. Since NMN can bypass these enzymes, NMN can potentially protect against retinal aging. Overall, while human studies are needed, these animal studies make NMN a promising candidate for the slowing of macular degeneration and perhaps preventing partial blindness.
Model and Dosage
Model: C57BL/6J male mice
Dosage: 300 mg/kg of NMN by intraperitoneal injection
Story Source
Ren C, Hu C, Wu Y, Li T, Zou A, Yu D, Shen T, Cai W, Yu J. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Cellular Senescence and Inflammation Caused by Sodium Iodate in RPE. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jul 18;2022:5961123. doi: 10.1155/2022/5961123. PMID: 35898618; PMCID: PMC9313989.