A new study has revealed that restoring NAD+ levels in the aging brain may be possible through the use of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) or small vesicles containing the NAD+ synthesizing enzyme NAMPT (eNampt). The research, conducted by scientists at Washington University, showed that treating aged mice with NMN or eNampt led to increased NAD+ levels in various regions of the hypothalamus, a brain region responsible for maintaining overall health and homeostasis.
The study utilized a novel method to accurately measure NAD+ levels in the small subregions of the hypothalamus, and the results showed that NAD+ levels decline significantly in three of the four measured areas in aged mice. The researchers found that a single shot of 300 mg/kg of NMN was enough to restore NAD+ levels in all three regions. Injecting aged mice with small vesicles from young mice containing NAMPT also resulted in nearly a 50% increase in NAD+ levels in the hypothalamus.
The findings of the study open up the possibility of future research on the effects of reduced NAD+ in the hypothalamus and other brain regions. The results also confirm that NMN is an effective method of replenishing NAD+ levels in the hypothalamus of aged mice, which can help maintain brain health and prevent cognitive decline.
In conclusion, the study highlights the importance of NAD+ in preserving brain health, especially in aging. The new method of measuring NAD+ levels in small tissues and the positive results of NMN supplementation offer hope for the future of brain health and wellness.
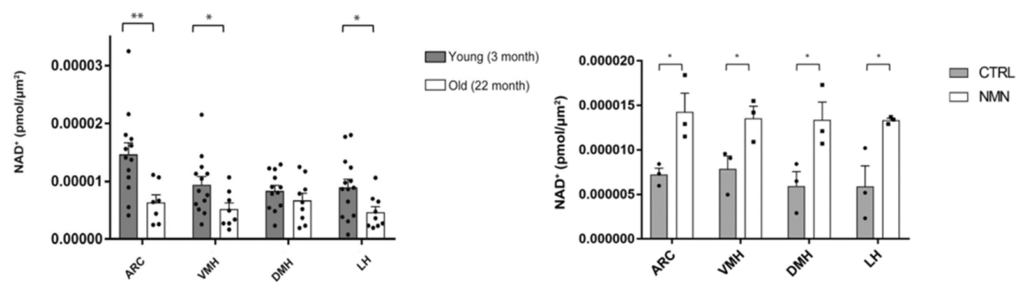
(Imai et al., 2023 | NPJ Aging) NMN attenuates falling NAD+ levels in four subregions of the hypothalamus. (Left) compared to young mice (grey), aged mice (white) show declining NAD+ levels in the arcuate nucleus (ARC), ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH), and lateral hypothalamus (LH) of the hypothalamus. (Right) NMN (white) increases NAD+ levels in all four hypothalamic subregions: ARC, VMH, LH, and dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH).
NAMPT-Containing Vesicles Boost Hypothalamic NAD+ Levels
NAMPT has been widely recognized as an effective NAD+ booster in various tissues and a promoter of longevity. Previous studies have shown that transplanting small vesicles from young mice into aged mice can increase NAD+ levels and extend lifespan. With this in mind, the researchers, Imai and colleagues, aimed to investigate the effects of similar vesicles on NAD+ levels in the hypothalamus.
The results showed that injecting aged mice with vesicles containing NAMPT from young mice resulted in a substantial increase in NAD+ levels in the hypothalamus. These findings suggest that these vesicles have potent NAD+-enhancing properties in the hypothalamus and raise the possibility that this treatment could reverse age-related changes in sensory processing and emotional control in the hypothalamus.
In conclusion, NAMPT-containing vesicles hold promise as a treatment for boosting NAD+ levels in the hypothalamus and may have potential for alleviating age-related changes in the brain. Further research is needed to fully understand the impact of this treatment on aging and brain health.
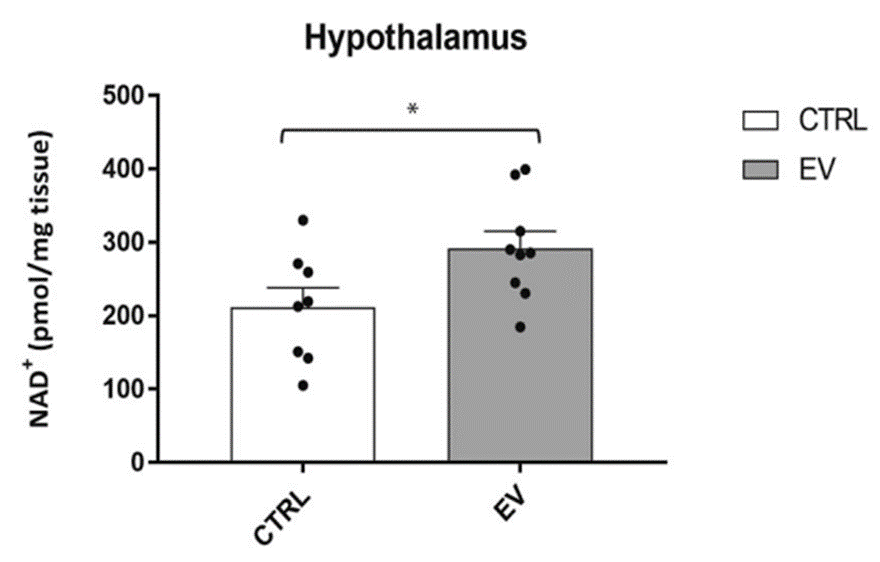
(Imai et al., 2023 | NPJ Aging) NAMPT-containing vesicles raise hypothalamic NAD+ levels. Compared to untreated controls (CTRL), aged mice treated with NAMPT-containing vesicles from young mice (EV) have around 50% more hypothalamic NAD+.
NMN and eNAMPT as Possible Treatments for Brain Aging
Thanks to the new method developed by Imai and colleagues for accurately measuring hypothalamic NAD+ levels, we now have the means to monitor brain aging and potentially discover new therapies. Our brains inevitably suffer a decline in function as we age, due to constant damage from stressors like inflammation and DNA damage, which rely on NAD+ for protection. Therefore, finding ways to increase NAD+ in various tissues is critical to slowing down aging and preserving organ function.
The study results show that NMN and eNAMPT can effectively raise NAD+ levels in the aged hypothalamus, suggesting that these treatments could mitigate the effects of brain aging, such as poor sleep, decreased physical ability, and diminished cognition. However, further research is needed to validate these findings.
Model and Dosage
Model: C57BL/6J mice
Dosage: 300 mg/kg NMN intraperitoneal injection at 22 months of age
Story Source
Johnson, S., Yoshioka, K., Brace, C.S. et al. Quantification of localized NAD+ changes reveals unique specificity of NAD+ regulation in the hypothalamus. npj Aging 9, 1 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41514-023-00098-1
https://www.nmn.com/news/washington-university-study-shows-nmn-replenishes-nad-in-the-aging-brain